From Passover Seders to Jewish foods and life-cycle milestones such as bar and bat mitzvahs, some aspects of Jewish religious life and culture are widespread among American Jews. But other religious expressions – such as regular attendance at synagogue services and belief in God as described in the Bible – are much less common, according to a new Pew Research Center survey.
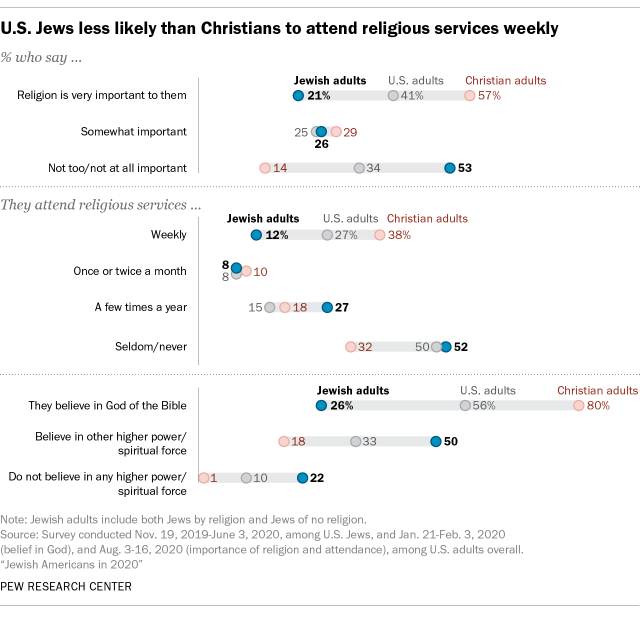
In fact, based on these more traditional measures of religious observance, Jews in the United States are far less religious than U.S. Christians and Americans overall.
Pew Research Center conducted this study to explore the breadth and diversity of Jewish Americans’ religious experiences. This survey represents the Center’s most comprehensive, in-depth study of the subject, drawing on 4,718 U.S. adults who identify as Jewish, including 3,836 Jews by religion and 882 Jews of no religion. The survey was administered online and by mail by Westat, from Nov. 19, 2019, to June 3, 2020. Respondents were drawn from a national, stratified random sampling of residential mailing addresses, which included addresses from all 50 states and the District of Columbia. No lists of common Jewish names, membership rolls of Jewish organizations or other indicators of Jewishness were used to draw the sample.
The sample is nationally representative and was weighted to align with demographic benchmarks for the U.S. adult population from the Census Bureau as well as a set of modeled estimates for the religious and demographic composition of eligible adults within the larger U.S. adult population. Here are the questions used for the report, along with responses, and its methodology.
For example, 12% of U.S. Jewish adults say they attend religious services weekly or more often, compared with 27% of the general public and 38% of U.S. Christians. And 21% of Jewish adults say religion is very important in their lives, compared with 41% of U.S. adults overall and 57% of Christians.
There are even bigger gaps when it comes to belief in God. About a quarter of Jews (26%) say they believe in God as described in the Bible, compared with more than half of U.S. adults overall (56%) and eight-in-ten Christians. Jews are more likely than U.S. adults overall (50% vs. 33%) to say they believe in some other spiritual force or higher power, but not in God as described in the Bible. Jewish adults also are twice as likely as the general public to say they do not believe in any kind of higher power or spiritual force in the universe (22% vs. 10%).
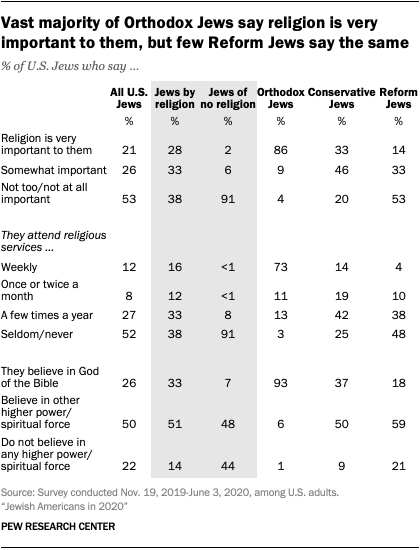
Orthodox Jews – who make up 9% of all U.S. Jews – are a notable exception. They are among the most highly religious groups in U.S. society by these measures. For example, 86% of Orthodox Jews say religion is very important in their lives, as do 78% of Black Protestants and 76% of White evangelical Protestants, two of the most highly religious Christian subgroups. Orthodox Jews (93%) also are about as likely as White evangelicals (94%) and Black Protestants (88%) to say they believe in God as described in the Bible.
Conservative and Reform Jews, who together make up 54% of U.S. Jews, are much less religious than Orthodox Jews by these measures. A third of Conservative Jews and 14% of Reform Jews say religion is very important in their lives. Moreover, 37% of Conservative Jews and 18% of Reform Jews believe in God as described in the Bible.
In analyzing the survey results, Pew Research Center also distinguished between two sets of respondents: those who say their religion is Jewish (referred to as “Jews by religion”) and those who describe themselves religiously as atheist, agnostic or nothing in particular, but who have a Jewish parent or were raised Jewish and still identify as Jewish in ways other than religion, such as culturally, ethnically or because of their family background (referred to as “Jews of no religion”). By these definitions, 73% of U.S. Jews are Jews by religion, while 27% are Jews of no religion.
Not surprisingly, Jews of no religion are much less religious than Jews by religion, at least by some standard measures. Fewer than 1% of Jews of no religion say they attend religious services at least weekly, compared with 16% of Jews by religion. And while 6% of Jews of no religion say religion is very important to them, the share is much higher (33%) among Jews by religion.
The fact that U.S. Jews as a whole are less likely than Americans overall to say religion is very important to them does not necessarily mean their Jewish identity is not meaningful to them. In fact, twice as many Jews say “being Jewish” is very important to them as say their religion is very important to them (42% vs. 21%). More than half of Jews by religion (55%) say being Jewish is very important to them, compared with just 7% of Jews of no religion.
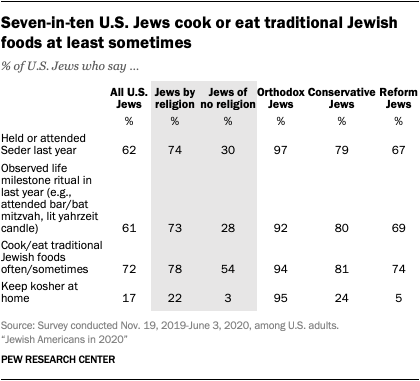
Both Jews by religion and Jews of no religion are more likely to engage with Judaism in other ways. Roughly six-in-ten Jewish Americans overall say they held or attended a Passover Seder in the year prior to the survey, including 74% of Jews by religion and 30% of Jews of no religion. Similar shares in both groups say they observed a life milestone such as a bar or bat mitzvah during that period. And about eight-in-ten Jews by religion (78%) say they often or sometimes cook or eat traditional Jewish foods, while roughly half of Jews of no religion (54%) say this.
Eating traditional Jewish foods is not to be mistaken with keeping kosher: Just 17% of U.S. Jews say they keep kosher in their homes, including 22% of Jews by religion and 3% of Jews of no religion. The vast majority of Orthodox Jews (95%) keep kosher at home, compared with 24% of Conservative Jews and 5% of Reform Jews.
Note: Here are the questions used for the report, along with responses, and its methodology.