
For the latest survey data on social media and tech use among teens, see “Teens, Social Media, and Technology 2023.”
Until recently, Facebook
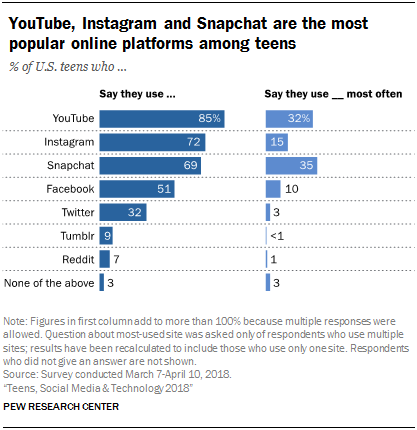
had dominated the social media landscape among America’s youth – but it is no longer the most popular online platform among teens, according to a new Pew Research Center survey. Today, roughly half (51%) of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 say they use Facebook, notably lower than the shares who use YouTube, Instagram or Snapchat.
This shift in teens’ social media use is just one example of how the technology landscape for young people has evolved since the Center’s last survey of teens and technology use in 2014-2015. Most notably, smartphone ownership has become a nearly ubiquitous element of teen life: 95% of teens now report they have a smartphone or access to one. These mobile connections are in turn fueling more-persistent online activities: 45% of teens now say they are online on a near-constant basis.
The survey also finds there is no clear consensus among teens about the effect that social media has on the lives of young people today. Minorities of teens describe that effect as mostly positive (31%) or mostly negative (24%), but the largest share (45%) says that effect has been neither positive nor negative.
These are some of the main findings from the Center’s survey of U.S. teens conducted March 7-April 10, 2018. Throughout the report, “teens” refers to those ages 13 to 17.
Facebook is no longer the dominant online platform among teens
The social media landscape in which teens reside looks markedly different than it did as recently as three years ago. In the Center’s 2014-2015 survey of teen social media use, 71% of teens reported being Facebook users. No other platform was used by a clear majority of teens at the time: Around half (52%) of teens said they used Instagram, while 41% reported using Snapchat.
In 2018, three online platforms other than Facebook – YouTube, Instagram and Snapchat – are used by sizable majorities of this age group. Meanwhile, 51% of teens now say they use Facebook. The shares of teens who use Twitter and Tumblr are largely comparable to the shares who did so in the 2014-2015 survey.
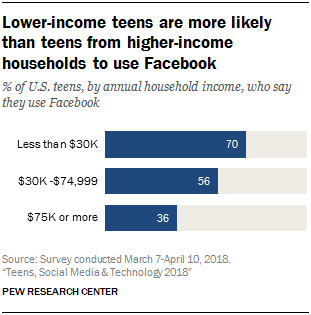
For the most part, teens tend to use similar platforms regardless of their demographic characteristics, but there are exceptions. Notably, lower-income teens are more likely to gravitate toward Facebook than those from higher-income households – a trend consistent with previous Center surveys. Seven-in-ten teens living in households earning less than $30,000 a year say they use Facebook, compared with 36% whose annual family income is $75,000 or more. (For details on social media platform use by different demographic groups, see Appendix A.)
It is important to note there were some changes in question wording between Pew Research Center’s 2014-2015 and 2018 surveys of teen social media use. YouTube and Reddit were not included as options in the 2014-2015 survey but were included in the current survey. In addition, the 2014-2015 survey required respondents to provide an explicit response for whether or not they used each platform, while the 2018 survey presented respondents with a list of sites and allowed them to select the ones they use.1 Even so, it is clear the social media environment today revolves less around a single platform than it did three years ago.2
When it comes to which one of these online platforms teens use the most, roughly one-third say they visit Snapchat (35%) or YouTube (32%) most often, while 15% say the same of Instagram. By comparison, 10% of teens say Facebook is their most-used online platform, and even fewer cite Twitter, Reddit or Tumblr as the site they visit most often.
Again, lower-income teens are far more likely than those from higher income households to say Facebook is the online platform they use most often (22% vs. 4%). There are also some differences related to gender and to race and ethnicity when it comes to teens’ most-used sites. Girls are more likely than boys to say Snapchat is the site they use most often (42% vs. 29%), while boys are more inclined than girls to identify YouTube as their go-to platform (39% vs. 25%). Additionally, white teens (41%) are more likely than Hispanic (29%) or black (23%) teens to say Snapchat is the online platform they use most often, while black teens are more likely than whites to identify Facebook as their most used site (26% vs. 7%).
Teens have mixed views on the impact of social media on their lives
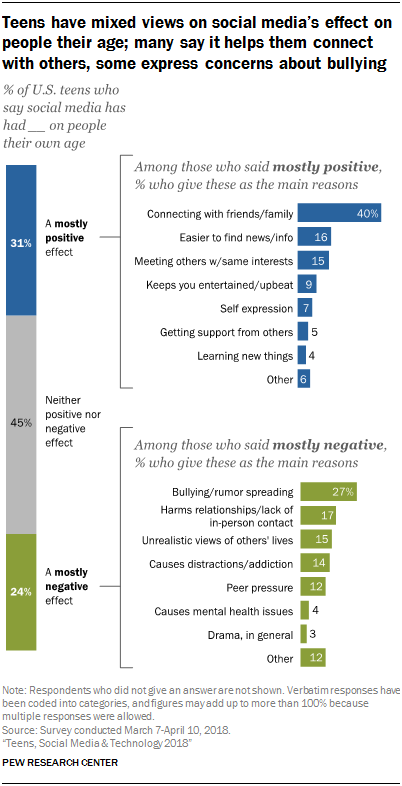
Despite the nearly ubiquitous presence of social media in their lives, there is no clear consensus among teens about these platforms’ ultimate impact on people their age. A plurality of teens (45%) believe social media has a neither positive nor negative effect on people their age. Meanwhile, roughly three-in-ten teens (31%) say social media has had a mostly positive impact, while 24% describe its effect as mostly negative.
Given the opportunity to explain their views in their own words, teens who say social media has had a mostly positive effect tended to stress issues related to connectivity and connection with others. Some 40% of these respondents said that social media has had a positive impact because it helps them keep in touch and interact with others. Many of these responses emphasize how social media has made it easier to communicate with family and friends and to connect with new people:
“I think social media have a positive effect because it lets you talk to family members far away.” (Girl, age 14)
“I feel that social media can make people my age feel less lonely or alone. It creates a space where you can interact with people.” (Girl, age 15)
“It enables people to connect with friends easily and be able to make new friends as well.” (Boy, age 15)
Others in this group cite the greater access to news and information that social media facilitates (16%), or being able to connect with people who share similar interests (15%):
“My mom had to get a ride to the library to get what I have in my hand all the time. She reminds me of that a lot.” (Girl, age 14)
“It has given many kids my age an outlet to express their opinions and emotions, and connect with people who feel the same way.” (Girl, age 15)
Smaller shares argue that social media is a good venue for entertainment (9%), that it offers a space for self-expression (7%) or that it allows teens to get support from others (5%) or to learn new things in general (4%).
“Because a lot of things created or made can spread joy.” (Boy, age 17)
“[Social media] allows us to communicate freely and see what everyone else is doing. [It] gives us a voice that can reach many people.” (Boy, age 15)
“We can connect easier with people from different places and we are more likely to ask for help through social media which can save people.” (Girl, age 15)
There is slightly less consensus among teens who say social media has had a mostly negative effect on people their age. The top response (mentioned by 27% of these teens) is that social media has led to more bullying and the overall spread of rumors.
“Gives people a bigger audience to speak and teach hate and belittle each other.” (Boy, age 13)
“People can say whatever they want with anonymity and I think that has a negative impact.” (Boy, age 15)
“Because teens are killing people all because of the things they see on social media or because of the things that happened on social media.” (Girl, age 14)
Meanwhile, 17% of these respondents feel these platforms harm relationships and result in less meaningful human interactions. Similar shares think social media distorts reality and gives teens an unrealistic view of other people’s lives (15%), or that teens spend too much time on social media (14%).
“It has a negative impact on social (in-person) interactions.” (Boy, age 17)
“It makes it harder for people to socialize in real life, because they become accustomed to not interacting with people in person.” (Girl, age 15)
“It provides a fake image of someone’s life. It sometimes makes me feel that their life is perfect when it is not.” (Girl, age 15)
“[Teens] would rather go scrolling on their phones instead of doing their homework, and it’s so easy to do so. It’s just a huge distraction.” (Boy, age 17)
Another 12% criticize social media for influencing teens to give in to peer pressure, while smaller shares express concerns that these sites could lead to psychological issues or drama.
 Vast majority of teens have access to a home computer or smartphone
Vast majority of teens have access to a home computer or smartphone
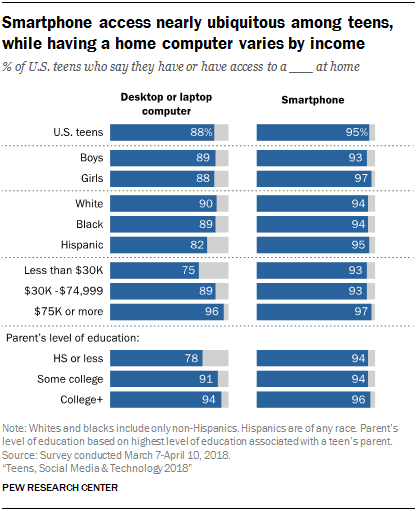
Some 95% of teens now say they have or have access to a smartphone, which represents a 22-percentage-point increase from the 73% of teens who said this in 2014-2015. Smartphone ownership is nearly universal among teens of different genders, races and ethnicities and socioeconomic backgrounds.
A more nuanced story emerges when it comes to teens’ access to computers. While 88% of teens report having access to a desktop or laptop computer at home, access varies greatly by income level. Fully 96% of teens from households with an annual income of $75,000 or more per year say they have access to a computer at home, but that share falls to 75% among those from households earning less than $30,000 a year.
Computer access also varies by the level of education among parents. Teens who have a parent with a bachelor’s degree or more are more likely to say they have access to a computer than teens whose parents have a high school diploma or less (94% vs. 78%).
A growing share of teens describe their internet use as near-constant
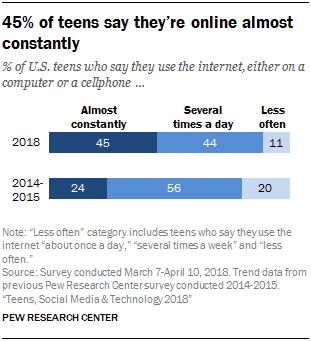
As smartphone access has become more prevalent, a growing share of teens now report using the internet on a near-constant basis. Some 45% of teens say they use the internet “almost constantly,” a figure that has nearly doubled from the 24% who said this in the 2014-2015 survey. Another 44% say they go online several times a day, meaning roughly nine-in-ten teens go online at least multiple times per day.
There are some differences in teens’ frequency of internet use by gender, as well as race and ethnicity. Half of teenage girls (50%) are near-constant online users, compared with 39% of teenage boys. And Hispanic teens are more likely than whites to report using the internet almost constantly (54% vs. 41%).
A majority of both boys and girls play video games, but gaming is nearly universal for boys
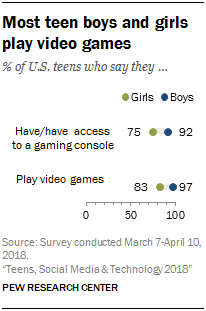
Overall, 84% of teens say they have or have access to a game console at home, and 90% say they play video games of any kind (whether on a computer, game console or cellphone). While a substantial majority of girls report having access to a game console at home (75%) or playing video games in general (83%), those shares are even higher among boys. Roughly nine-in-ten boys (92%) have or have access to a game console at home, and 97% say they play video games in some form or fashion.
There has been growth in game console ownership among Hispanic teens and teens from lower-income families since the Center’s previous study of the teen technology landscape in 2014-2015. The share of Hispanics who say they have access to a game console at home grew by 10 percentage points during this time period. And 85% of teens from households earning less than $30,000 a year now say they have a game console at home, up from 67% in 2014-2015.