Worldwide, more than eight-in-ten people identify with a religious group. A comprehensive demographic study of more than 230 countries and territories conducted by the Pew Research Center’s Forum on Religion & Public Life estimates that there are 5.8 billion religiously affiliated adults and children around the globe, representing 84% of the 2010 world population of 6.9 billion.
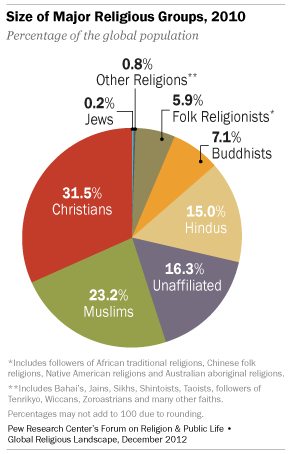
The demographic study – based on analysis of more than 2,500 censuses, surveys and population registers – finds 2.2 billion Christians (32% of the world’s population), 1.6 billion Muslims (23%), 1 billion Hindus (15%), nearly 500 million Buddhists (7%) and 14 million Jews (0.2%) around the world as of 2010. In addition, more than 400 million people (6%) practice various folk or traditional religions, including African traditional religions, Chinese folk religions, Native American religions and Australian aboriginal religions. An estimated 58 million people – slightly less than 1% of the global population – belong to other religions, including the Baha’i faith, Jainism, Sikhism, Shintoism, Taoism, Tenrikyo, Wicca and Zoroastrianism, to mention just a few.1
At the same time, the new study by the Pew Forum also finds that roughly one-in-six people around the globe (1.1 billion, or 16%) have no religious affiliation. This makes the unaffiliated the third-largest religious group worldwide, behind Christians and Muslims, and about equal in size to the world’s Catholic population. Surveys indicate that many of the unaffiliated hold some religious or spiritual beliefs (such as belief in God or a universal spirit) even though they do not identify with a particular faith. (See Religiously Unaffiliated.)
Geographic Distribution
The geographic distribution of religious groups varies considerably. Several religious groups are heavily concentrated in the Asia-Pacific region, including the vast majority of Hindus (99%), Buddhists (99%), adherents of folk or traditional religions (90%) and members of other world religions (89%).
Three-quarters of the religiously unaffiliated (76%) also live in the massive and populous Asia- Pacific region. Indeed, the number of religiously unaffiliated people in China alone (about 700 million) is more than twice the total population of the United States.
The Asia-Pacific region also is home to most of the world’s Muslims (62%). About 20% of Muslims live in the Middle East and North Africa, and nearly 16% reside in sub-Saharan Africa.
Of the major religious groups covered in this study, Christians are the most evenly dispersed. Roughly equal numbers of Christians live in Europe (26%), Latin America and the Caribbean (24%) and sub-Saharan Africa (24%).
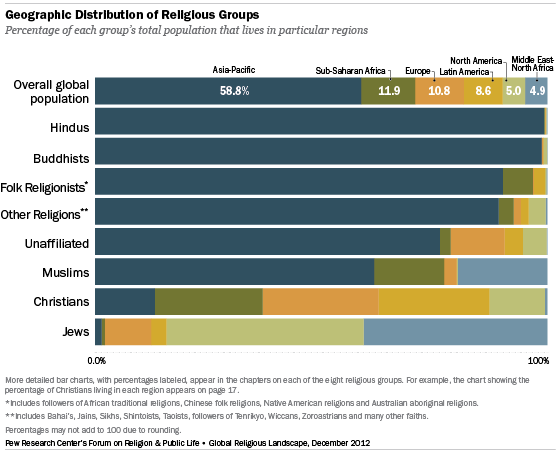
A plurality of Jews (44%) live in North America, while about four-in-ten (41%) live in the Middle East and North Africa – almost all of them in Israel.
Living as Majorities and Minorities
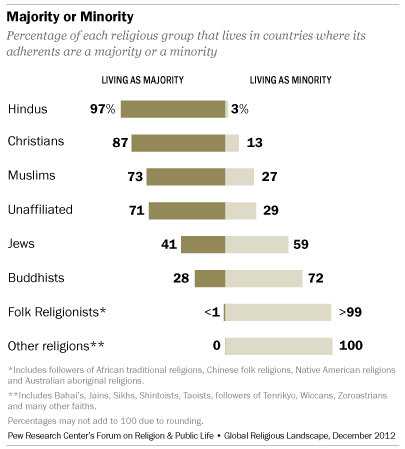
Nearly three-quarters (73%) of the world’s people live in countries in which their religious group makes up a majority of the population. Only about a quarter (27%) of all people live as religious minorities. (This figure does not include subgroups of the eight major groups in this study, such as Shia Muslims living in Sunni-majority countries or Catholics living in Protestant-majority countries.)
Overwhelmingly, Hindus and Christians tend to live in countries where they are in the majority. Fully 97% of all Hindus live in the world’s three Hindu-majority countries (India, Mauritius and Nepal), and nearly nine-in-ten Christians (87%) are found in the world’s 157 Christian-majority countries. (To see the religious composition of each country, see Religious Composition by Country table.)
Though by smaller margins, most Muslims (73%) and religiously unaffiliated people (71%) also live in countries in which they are the predominant religious group. Muslims are a majority in 49 countries, including 19 of the 20 countries in the Middle East and North Africa. The religiously unaffiliated make up a majority of the population in six countries, of which China is by far the largest. (The others are the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hong Kong, Japan and North Korea.)
Most members of the other major religious groups live in countries in which they are in the minority. Seven-in-ten Buddhists (72%), for example, live as religious minorities. Just three-in-ten (28%) live in the seven countries where Buddhists are in the majority: Bhutan, Burma (Myanmar), Cambodia, Laos, Mongolia, Sri Lanka and Thailand.
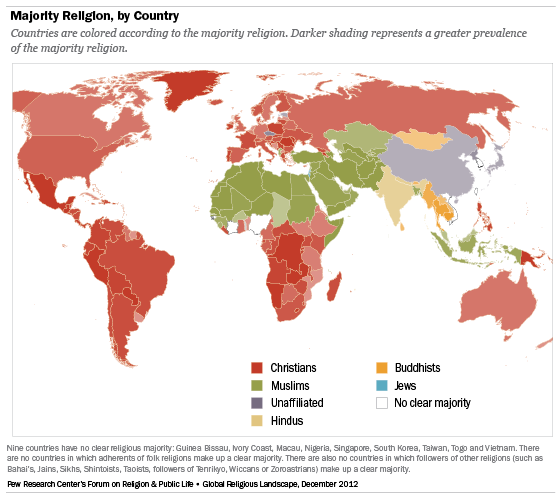
Israel is the only country with a Jewish majority. There are no countries where members of other religions (such as Baha’is, Jains, Shintoists, Sikhs, Taoists, followers of Tenrikyo, Wiccans and Zoroastrians) make up a majority of the population. There are also no countries where people who identify with folk or traditional religions clearly form a majority.2
Young and Old
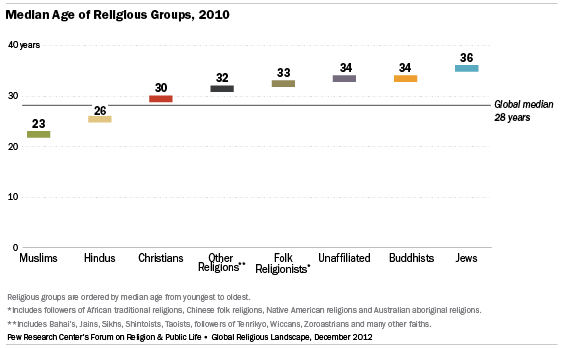
Some religions have much younger populations, on average, than others. In part, the age differences reflect the geographic distribution of religious groups. Those with a large share of adherents in fast-growing, developing countries tend to have younger populations. Those concentrated in China and in advanced industrial countries, where population growth is slower, tend to be older.
The median age of two major groups – Muslims (23 years) and Hindus (26) – is younger than the median age of the world’s overall population (28).3 All the other groups are older than the global median. Christians have a median age of 30, followed by members of other religions (32), adherents of folk or traditional religions (33), the religiously unaffiliated (34) and Buddhists (34). Jews have the highest median age (36), more than a dozen years older than the youngest group, Muslims.
About the Study
These are among the key findings of a new study of the global religious landscape conducted by the Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life as part of the Pew-Templeton Global Religious Futures project, which analyzes religious change and its impact on societies around the world.
The demographic study explores the size, geographic distribution and median age of eight major religious groups – including the unaffiliated – that together represent 100% of the estimated 2010 global population. The study is based on a country-by-country analysis of data from more than 2,500 national censuses, large-scale surveys and official population registers that were collected, evaluated and standardized by the Pew Forum’s demographers and other research staff.4 Many countries have recently conducted a national census or are in the midst of doing so. Therefore, new data are likely to emerge over the next few years. However, a datacollection cut-off had to be made at some point; this report is based on information available as of early 2012.5
For estimates of the religious composition of individual countries, see Religious Composition by Country table. For details on the methodology used to produce estimates of religious populations in 232 countries and territories, see Appendix A. For a list of data sources by country, see Appendix B.
To see each country’s and territory’s population broken down by number and percentage into the eight major religious groups in the study, see the sortable tables at http://features.pewresearch.org/religion/grl/population-number.php.
There are some minor differences between the estimates presented in this study and previous Pew Forum estimates of Christian and Muslim populations around the world. These differences reflect the availability of new data sources, such as recently released censuses in a few countries, and the use of population growth projections to update estimates in countries with older primary sources. (For more details, see the Methodology.)
Defining the Religious Groups
This study is based on self-identification. It seeks to estimate the number of people around the world who view themselves as belonging to various religious groups. It does not attempt to measure the degree to which members of these groups actively practice their faiths or how religious they are.
In order to obtain statistics that are comparable across countries, the study attempts to count groups and individuals who self-identify as members of five widely recognized world religions – Buddhists, Christians, Hindus, Muslims and Jews – as well as people associated with three other religious categories that may be less familiar:
Folk or Traditional Religions
Folk religions are closely tied to a particular people, ethnicity or tribe. In some cases, elements of other world religions are blended with local beliefs and customs. These faiths often have no formal creeds or sacred texts. Examples of folk religions include African traditional religions, Chinese folk religions, Native American religions and Australian aboriginal religions.
The Religiously Unaffiliated
The religiously unaffiliated population includes atheists, agnostics and people who do not identify with any particular religion in surveys. However, many of the religiously unaffiliated do hold religious or spiritual beliefs. For example, various surveys have found that belief in God or a higher power is shared by 7% of unaffiliated Chinese adults, 30% of unaffiliated French adults and 68% of unaffiliated U.S. adults.6
Other Religions
The “other religions” category is diverse and comprises groups not classified elsewhere. This category includes followers of religions that often are not measured separately in censuses and surveys: the Baha’i faith, Jainism, Shintoism, Sikhism, Taoism, Tenrikyo, Wicca, Zoroastrianism and many other religions. Because of the lack of data on these faiths in many countries, the Pew Forum has not attempted to estimate the size of individual religions within this category, though some rough estimates are available from other sources. (See Spotlight on Other Religions.)
Roadmap to the Report
These and other findings are discussed in more detail in the remainder of this report, which is divided into eight sections – one for each of the major religious groupings, in order of size:
To discuss the geographic distribution of religious groups, this report divides the world into six major regions: Asia and the Pacific, Europe, Latin America and the Caribbean, the Middle East and North Africa, North America and sub-Saharan Africa. For a list of countries in each region, see the Methodology.
Footnotes:
1 Although some faiths in the “other religions” category have millions of adherents around the world, censuses and surveys in many countries do not measure them specifically. Estimates of the global size of these faiths generally come from other sources, such as the religious groups themselves. By far the largest of these groups are Sikhs, who number about 25 million, according to the World Religion Database. For more information, see Spotlight on Other Religions. (return to text)
2 For a discussion of the challenges of measuring the pervasiveness of folk or traditional religions, see the section on Folk Religionists. (return to text)
3 The median in a population is the midpoint when the entire population is ordered by some characteristic, such as age or income. If everyone alive in 2010 lined up from youngest to oldest, the person in the middle (the median) would be 28 years old. (return to text)
4 A population register is a list of all permanent residents of a country. See the United Nations Statistics Division’s description of population registers (http://unstats.un.org/unsd/demographic/sources/popreg/popregmethods.htm). (return to text)
5 For instance, in December 2012, just before the release of this report, new religion data were released from the 2011 Census of England and Wales. The new data suggest a slightly different religious landscape than the estimate made by this study for the broader United Kingdom (England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland), which is based primarily on the 2010 Annual Population Survey carried out by the U.K.’s Office for National Statistics.(return to text)
6 For more information on the beliefs and practices of religiously unaffiliated adults in the United States, see the Pew Forum’s October 2012 report “‘Nones’ on the Rise.” The Pew Forum’s U.S. surveys typically ask about belief in “God or a universal spirit.” French results are based on a Pew Forum analysis of 2008 International Social Survey Programme (ISSP) data. The ISSP survey asks about belief in God or a “higher power of some kind.” Chinese results are based on a Pew Forum analysis of the 2007 Spiritual Life Study of Chinese Residents, conducted by the Chinese polling firm Horizon. In China, the belief in God statistic measures belief in God, gods, spirits, ghosts or Buddha. (return to text)