A majority of Americans consider climate change a priority today so that future generations can have a sustainable planet, and this view is held across generations.
Looking to the future, the public is closely divided on what it will take to address climate change: While about half say it’s likely major lifestyle changes in the U.S. will be needed to deal with climate change impacts, almost as many say it’s more likely new developments in technology will address most of the problems cause by climate change.
On policy, majorities prioritize the use of renewable energy and back the expanded use of specific sources like wind and solar. Americans offer more support than opposition to a range of policies aimed at reducing the effects of climate change, including key climate-related aspects of President Joe Biden’s recent infrastructure proposal. Still, Americans do not back a complete break with carbon: A majority says oil and gas should still be part of the energy mix in the U.S., and about half oppose phasing out gas-powered vehicles by 2035.
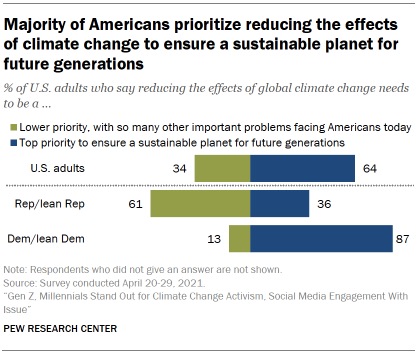
Overall, 64% of U.S. adults say reducing the effects of climate change needs to be “a top priority to ensure a sustainable planet for future generations, even if that means fewer resources for addressing other important problems today.” By contrast, 34% say that reducing the effects of climate change needs to be “a lower priority, with so many other important problems facing Americans today, even if that means more climate problems for future generations.”
There are stark partisan differences over this sentiment. Nearly nine-in-ten Democrats (87%) say efforts to reduce the effects of climate change need to be prioritized today to ensure a sustainable planet. By contrast, 61% of Republicans say that efforts to reduce the effects of climate change need to be a lower priority, with so many other important problems facing Americans today. (Democrats and Republicans include those who lean to each party.)
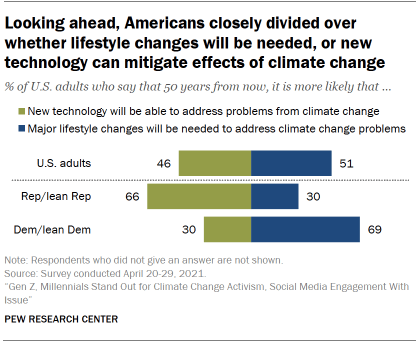
Asked to look to the future 50 years from now, 51% of Americans say it’s more likely that major changes to everyday life in the U.S. will be needed to address the problems caused by global climate change. By contrast, 46% say it’s more likely that new technology will be able to address most of the problems caused by global climate change.
Most Democrats (69%) expect that in 50 years major lifestyle changes in the U.S. will be needed to address the problems caused by climate change. By contrast, among Republicans, two-thirds (66%) say it’s likelier that new technology will be able to address most climate change problems in the U.S. Among Republicans, this view is widely held (81%) among the majority who do not see climate change as an important personal concern; Republicans who express greater personal concern about climate change are more likely to say major changes to everyday life in the future will be needed to address problems caused by climate change.
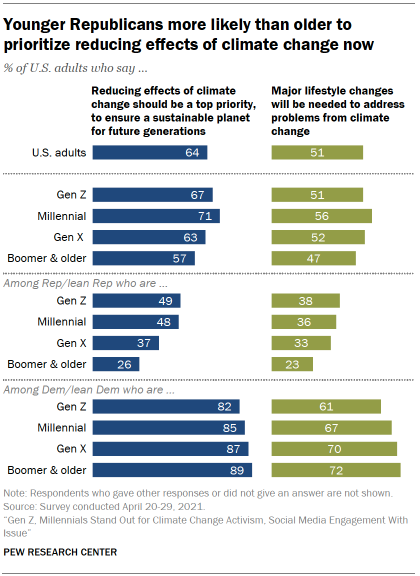
Overall, majorities across generations believe that climate change should be a top priority today to ensure a sustainable planet for future generations. Generational divisions are more prominent among Republicans than Democrats, however.
Among Republicans, about half of Gen Zers (49%) and Millennials (48%) give top priority to reducing the effect of climate change today, even if that means fewer resources to deal with other important problems. By contrast, majorities of Gen X (61%) and Baby Boomer and older Republicans (71%) say reducing the effects of climate change needs to a lower priority today, given the other problems Americans are facing.
Generational differences among Democrats on this question are modest, with clear majorities giving priority to dealing with climate change today.
Majority of Americans prioritize developing alternative energy sources, but only a third would phase out all fossil fuels
Burning fossil fuels for electricity and in cars and trucks are among the primary sources of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. Americans broadly favor increasing the use of renewable energy sources, but a majority reject the idea of phasing out fossil fuel energy sources completely. And Americans are about evenly divided on the idea of phasing out the production of new gasoline cars and trucks by 2035.
There are familiar partisan divisions over nearly every aspect of energy policy, particularly when it comes to fossil fuels. Political divides have widened over the past year as Republican support for alternative energy sources – including wind and solar power – has fallen while support for expanding offshore oil drilling, hydraulic fracturing and coal mining has ticked up.
Within both parties, Gen Zers and Millennials are more supportive of proposals to move away from fossil fuels than their older counterparts.
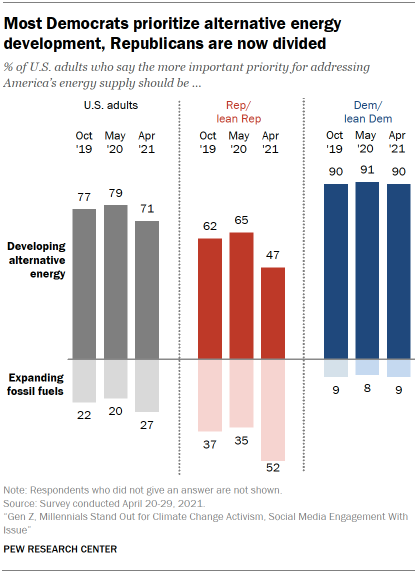
A majority of Americans (71%) continue to say that the U.S. should prioritize developing alternative energy, while a much smaller share (27%) prioritizes expanding the production of oil, coal and natural gas.
The share of Republicans who prioritize developing alternative energy sources over expanding the production of fossil fuels has fallen 18 percentage points in the past year. As a result, Republicans are now closely divided between these two energy priorities. Democrats remain near consensus levels in their support for prioritizing development of alternative energy levels.
Among Republicans, there are significant generational differences in support for increasing the development of renewable energy sources. Majorities of Gen Z (63%) and Millennial (62%) Republicans prioritize increased development of renewable sources, such as wind and solar. Smaller shares of Gen X Republicans (50%) and just 33% of Baby Boomer and older Republicans prioritize this approach over the expanding of fossil fuel development. For more details, including longer-term trends over time, see the Appendix.
Republicans and Democrats also differ over the best way to encourage reliance on renewable energy sources. Most Democrats (81%) continue to see a need for government regulations to increase reliance on renewable energy. On the other hand, two-thirds of Republicans (67%) say the private marketplace alone will be enough. See the Appendix for details.
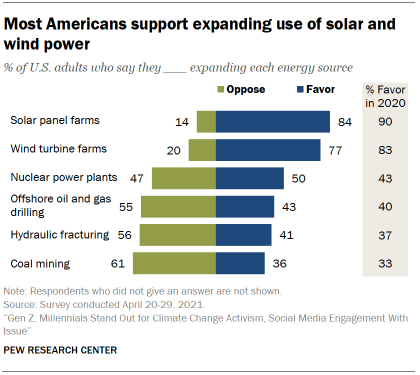
In keeping with support for prioritizing the development of renewable energy, most Americans favor expanding solar panel farms (84%) and wind turbine farms (77%). By contrast, majorities oppose more coal mining (61%), more hydraulic fracturing (56%) and more offshore oil and gas drilling (55%).
Americans are divided over expanding nuclear power: 50% favor more nuclear power plants, while 47% are opposed.
Republican support for expanding solar power is down 11 points in the last year (from 84% to 73%), and support for wind power has fallen 13 points (from 75% to 62%). Democrats’ widely held support for increasing both energy sources remains largely unchanged.
In addition, there has been an increase since 2020 in the shares of Republicans who support expanding hydraulic fracturing of natural gas (up 10 points), offshore oil and gas drilling (up 6 points) and coal mining (up 6 points). See the Appendix for details.
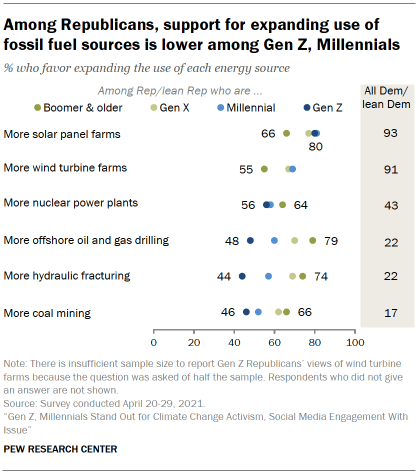
Even so, younger Republicans remain less likely than their older counterparts to support expanding fossil fuel sources, consistent with past Center surveys.
For instance, 79% of Baby Boomer and older Republicans support more offshore oil and gas drilling, while roughly half (48%) of Gen Z Republicans say the same (a difference of 31 points). There are similar divides over hydraulic fracturing, the primary extraction technique for natural gas (74% of Baby Boomer and older Republicans favor vs. 44% of Gen Z Republicans).
Nearly two-thirds of Americans support using a mix of fossil fuel and renewable energy sources, younger adults more inclined to phase out fossil fuels completely
While a large share of U.S. adults would prioritize alternative energy development over expanding the use of fossil fuels, most adults are not inclined to give up reliance on fossil fuels altogether.
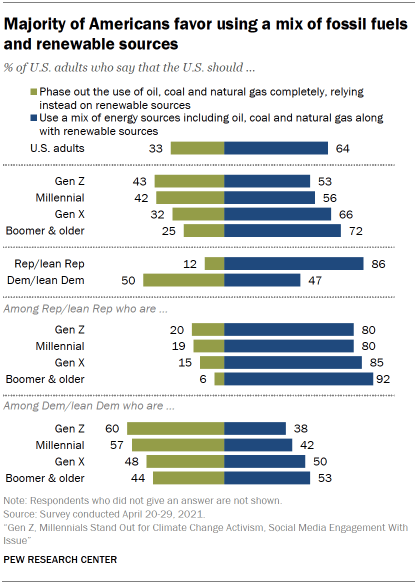
The survey finds 64% of Americans say they support ongoing use of oil, coal and natural gas as well as renewable energy sources, while a third (33%) say the country should phase out the use of fossil fuels completely.
There are sharp differences of opinion about this issue by party. Most Republicans (86%) say that the U.S. should rely on a mix of fossil fuel and renewable energy sources. Democrats are about evenly divided, with 47% in favor of using a mix of sources and 50% calling for a phase out of fossil fuels. About two-thirds of liberal Democrats (65%) support phasing out fossil fuels but fewer moderate and conservative Democrats say the same (39%).
There are also generational divisions on this issue, with younger generations more likely to support giving up fossil fuel use over time. In fact, majorities of Democratic Gen Zers (60%) and Millennials (57%) support phasing out fossil fuel use completely.
Americans are closely divided over phasing out gas-powered vehicles; Democrats, younger adults are more receptive to the idea
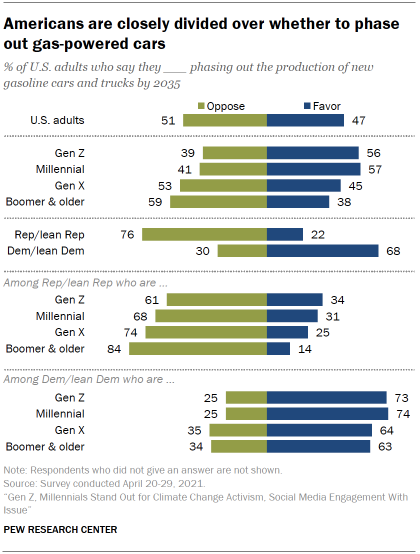
Climate advocates point to electric vehicles as a way to cut down on carbon emissions and reduce climate change. Americans are about equally divided on the idea of phasing out production of gasoline cars and trucks by 2035. A little under half (47%) say they would favor such a proposal, while 51% are opposed.
As with other proposals on climate and energy issues, partisans express opposing viewpoints. About two-thirds of Democrats (68%) support phasing out gasoline cars by 2035, while 76% of Republicans oppose this.
Most U.S. adults oppose oil drilling in ANWR but are more divided over Keystone XL decision
The issue of whether or not to allow oil and gas drilling in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge has long been a controversy in energy policy. Overall, most Americans (70%) oppose the idea, while 27% are in favor.
Nearly all Democrats (89%) say they oppose allowing oil and gas drilling in the ANWR. Republicans are about evenly divided, with half in favor of allowing this and 48% opposed.
One of Biden’s first actions as president was revoking the permit for the Keystone XL pipeline. The pipeline would have carried oil from Canada into the U.S.
About half of Americans (49%) say canceling the pipeline was the right decision, while 45% say it was the wrong decision.
Most Democrats (78%) say it was the right decision, while most Republicans (80%) say otherwise. See details in the Appendix.
But there are also generational dynamics in views about gasoline-powered vehicles, with younger adults more supportive than older adults of phasing out gas cars and trucks. Narrow majorities of Gen Zers (56%) and Millennials (57%) support such a proposal, compared with 38% of Baby Boomer and older Americans. This pattern holds within both parties, though sizable partisan divides remain across all generations. See the Appendix for a look at how these generational and partisan divides compare across measures.
The public is broadly familiar with electric vehicles: About nine-in-ten have heard either a lot (30%) or a little (62%) about them. When it comes to first-hand experience, 7% of adults say they currently have an electric or hybrid vehicle; 93% say they do not.
People who say they have heard a lot about electric vehicles are closely divided over the idea of phasing out gas-powered cars and trucks by a margin of 52% in favor to 48% opposed. Not surprisingly, those who currently own an electric or hybrid vehicle are largely in favor of this idea (68% vs. 31% opposed).
Broad public support for a number of policies to address climate change, including some proposed in Biden infrastructure plan
In late March, the Biden administration announced a $2 trillion infrastructure plan with several elements they argue would help reduce the effects of climate change. The new Center survey finds majorities of Americans support a number of proposals to address global climate change, including three specific elements in Biden’s infrastructure plan.
There are sharp partisan divisions over many of these proposals, as expected. In addition, there are concerns, particularly among Democrats, that Biden’s policy proposals will not go far enough in efforts to reduce the effects of climate change.
Majorities of U.S. adults support a range of approaches to address climate change
The new Center survey finds majorities back three specific elements of Biden’s infrastructure plan. More than seven-in-ten Americans (74%) favor a proposed requirement for power companies to use more energy from renewable sources, such as solar and wind, to reduce carbon emissions. A smaller majority – 62% – favors federal spending to build a network of electric vehicle charging stations across the country in order to increase the use of electric cars and trucks.
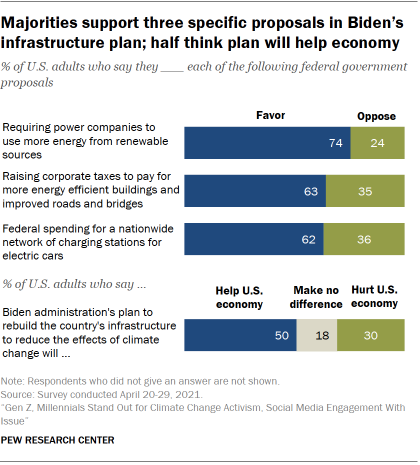
And 63% of Americans support the idea of raising corporate taxes to pay for more energy efficient buildings and improved roads and bridges, a key funding mechanism in Biden’s infrastructure proposal.
Biden has closely tied his climate-focused infrastructure proposals with economic and job growth. Half of U.S. adults think that the Biden administration’s plan to rebuild the nation’s infrastructure in ways that are aimed at reducing the effects of climate change will help the economy. Three-in-ten think this will hurt the economy, and 18% say it will make no difference.
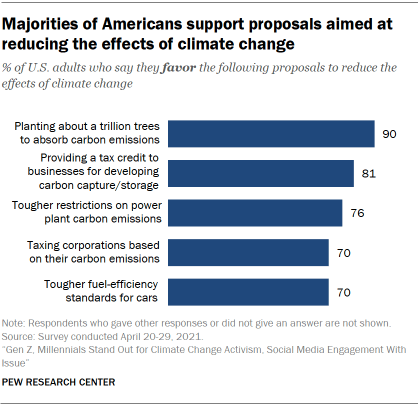
Americans continue to broadly support a number of longer-standing proposals to reduce the effects of climate change. Nine-in-ten Americans favor planting additional trees to absorb carbon dioxide emissions. About eight-in-ten (81%) favor providing a tax credit for businesses that develop technology that can capture and store carbon emissions before they enter the atmosphere. Both of these ideas were part of a set of policies supported by congressional Republicans last year.
Large majorities of Americans also favor tougher restrictions on power plant carbon emissions (76%), taxing corporations based on the amount of carbon emissions they produce (70%) and tougher fuel-efficiency standards for automobiles and trucks (70%).
54% of Democrats think Biden administration’s climate policies will not go far enough
Three months into the Biden administration, there is no clear consensus over the administration’s approach on climate change. About four-in-ten Americans (41%) think the Biden administration’s policies to reduce the effects of climate change will not go far enough. Roughly three-in-ten (29%) think the Biden administration will go too far, and a similar share (28%) say the administration’s approach will be about right.
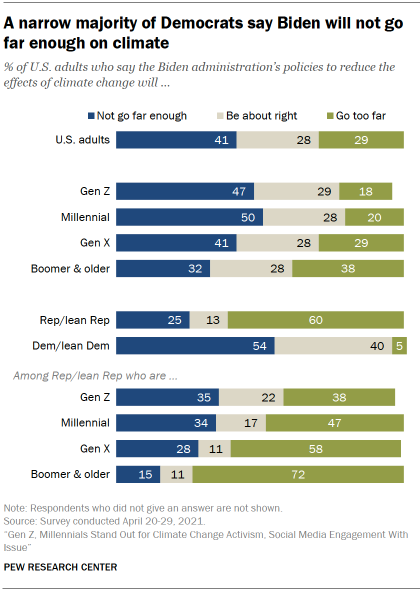
Republicans and Democrats have far different expectations for the Biden’s administration policies on climate change. A narrow majority of Democrats and those who lean to the Democratic Party (54%) –including 63% of liberal Democrats – think the administration’s policies will not go far enough to reduce the effects of climate change.
In contrast, six-in-ten Republicans and Republican-leaning independents say the Biden administration’s policies will go too far, including 74% of conservative Republicans.
There are some generational differences in views on this this issue among Republicans, in line with differences over the importance of addressing climate change. About as many Gen Z Republicans say Biden’s climate policies will not go far enough (35%) as say the policies will go too far (38%). By comparison, a 72% majority of Republicans in the Baby Boomer or older generations think the Biden administration will go too far on climate change.
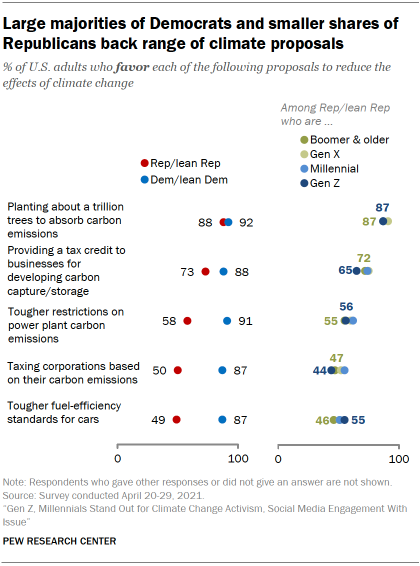
When it comes to views about proposals aimed at reducing climate change, however, there are few differences of opinion across generations among either party. Yet large differences remain between Republicans and Democrats overall.
Democrats’ views about five proposals aimed at reducing the effects of climate change are uniformly positive. Roughly 85% to 95% of Democrats support each.
Republicans and Republican leaners are most supportive of proposals to absorb carbon emissions by planting large numbers of trees (88%), followed by a proposal to provide a corporate tax credit for carbon-capture technology (73%). A majority of the GOP (58%) favor tougher restrictions on carbon emissions from power plants. About half of Republicans favor taxing corporate carbon emissions (50%) or tougher fuel-efficiency standards for cars and trucks (49%).
There are no divisions within the GOP by generation across these issues, though ideological divides are often sharp. For example, 65% of moderate and liberal Republicans favor tougher fuel-efficiency standards for cars and trucks, compared with 40% of conservative Republicans.
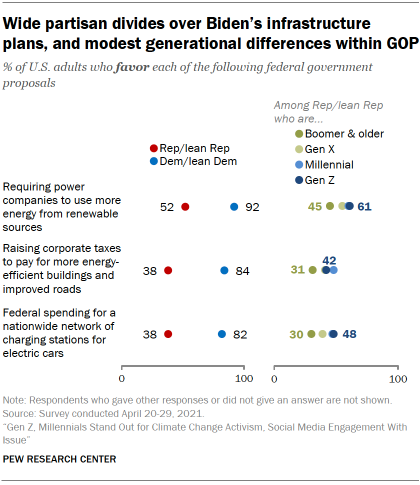
Republicans and Democrats are also deeply divided over climate-focused proposals in the Biden administration’s infrastructure plan.
Large majorities of Democrats favor requiring power companies to use more energy from renewable sources (92%), raising corporate taxes to pay for energy efficient buildings and improved roads (84%) and building a network of electric vehicle charging stations across the country (82%).
About half of Republicans (52%) support requiring power companies to use more energy from renewable sources. There is less support for federal spending to build a nationwide network of electric vehicle charging stations (38%). An equal share of Republicans (38%) support the idea of raising taxes on corporations to pay for more energy efficient buildings and better roads, although more moderates and liberals in the GOP (59%) than conservatives (27%) support this idea.
There is comparatively more support for these proposals among younger Republicans, particularly for federal spending to build electric vehicle charging stations and requirements for power plants to use more renewable sources.
Republicans and Democrats at odds over economic impact of Biden’s infrastructure plan
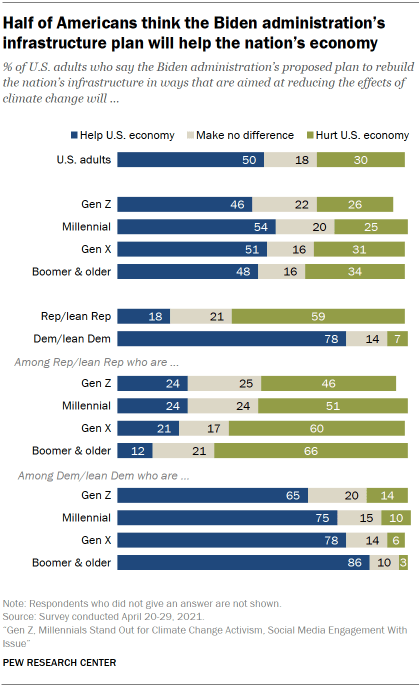
Democrats are largely optimistic that the Biden administration’s plan to rebuild the nation’s infrastructure in ways aimed at reducing the effects of climate change will help the economy. About eight-in-ten Democrats (78%) say this.
Among Republicans, a majority (59%) thinks this proposed plan will hurt the economy, while only about two-in-ten (18%) say it will help. Conservative Republicans (71%) are especially inclined to say the climate-focused infrastructure proposal will hurt the economy.
Generational differences are largely modest but occur in both parties. Baby Boomer Republicans are the most pessimistic about the plan’s economic impact, while Boomer Democrats are the most optimistic that the plan will help the economy.
What are important considerations to Americans in climate proposals?
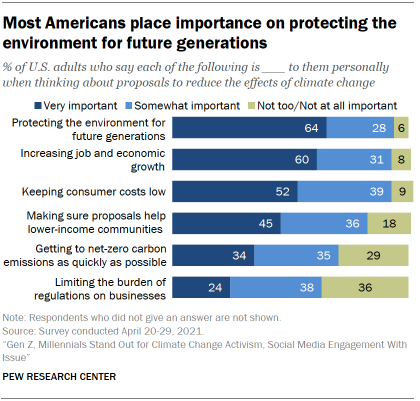
When it comes to proposals to reduce the effects of global climate change, protecting the environment for future generations and increasing jobs and economic growth are the top considerations Americans would like to see in policy proposals.
Asked to think about what is important to them in proposals to reduce the effects of climate change, 64% of the public says protecting the quality of the environment for future generations is a very important consideration to them personally; 28% say it’s somewhat important to them and just 6% say it’s not too or not at all important to them.
A majority (60%) also says that increasing job and economic growth is a very important consideration to them personally when it comes to proposals to reduce the effects of climate change.
About half (52%) say keeping consumer costs low is a very important consideration to them personally in climate proposals. Making sure proposals help lower-income communities is seen as a very important consideration by 45% of the public.
About a third (34%) say getting to net-zero carbon emissions as quickly as possible is a very important consideration to them personally. Joe Biden has set a goal for the U.S. to reach net-zero emissions by 2050.
Limiting the burden of regulations on businesses is seen as a very important climate policy consideration by 24% of the public – the lowest share who say this across the six items asked in the survey. However, majorities view all six factors, including limiting the regulatory burden on businesses, as at least somewhat important considerations in climate proposals.
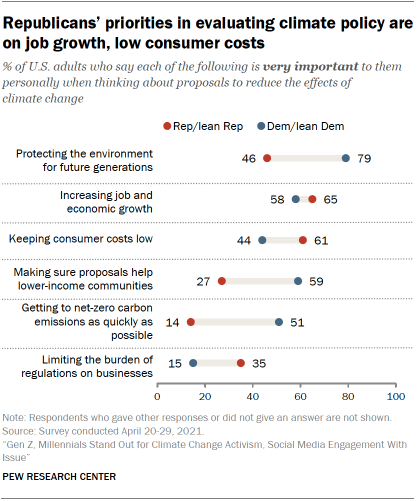
Partisans have differing priorities when it comes to climate change proposals. Among Republicans, increasing job and economic growth (65% very important) and keeping consumer costs low (61%) are their top considerations. Among Democrats, protecting the quality of the environment for future generations is their clear top consideration (79% very important), followed by making sure proposals help lower-income communities (59%) and increasing job and economic growth (58%). About half of Democrats (51%) say getting to net-zero carbon emissions as quickly as possible is very important to them.
Public sees actions from businesses, ordinary Americans as insufficient on climate change
Americans see a range of actors as falling short in efforts to help reduce the effects of global climate change. The public is broadly critical of the lack of action from large businesses and the energy industry – but also views elected officials, as well as ordinary Americans, as failing to do their part.
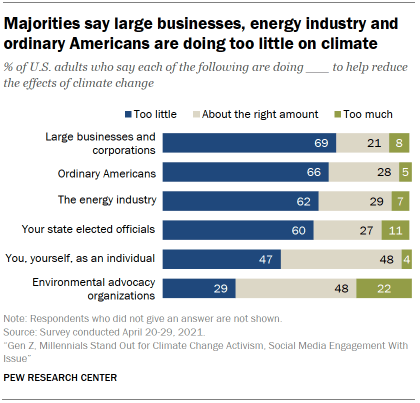
Nearly seven-in-ten adults (69%) say large businesses and corporations are doing too little to help reduce the effects of global climate change, while just 21% say they are doing about the right amount and very few (8%) say they are doing too much to address climate change. Similarly, a majority of the public (62%) says the energy industry is doing too little to help reduce the effects of global climate change.
The public also extends criticism on climate inaction to Americans themselves and the officials they vote into elected office. Overall, 66% say ordinary Americans are doing too little to help reduce the effects of climate change, and 60% say this about their state’s elected officials. A separate question that asks about the actions of the federal government across a range of environmental areas finds that 59% say the federal government is doing too little on climate change.
Americans are less critical of their own individual actions in helping to address climate change: Roughly half (48%) believe they, themselves, are doing about the right amount to help reduce the effects of climate change. Still, almost as many (47%) say they are doing too little to help.
When it comes to the role of environmental advocacy organizations, 48% say they are doing about the right amount to help reduce the effects of climate change, compared with 29% who say they are doing too little and 22% who say they are doing too much.
There are stark partisan differences in views of the role groups and individuals are playing to help reduce the effects of climate change. Large majorities of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say large businesses (85%), ordinary Americans (82%), the energy industry (80%) and their state elected officials (79%) are doing too little to help reduce climate change impacts. By contrast, about half of Republicans and Republican leaners or fewer say these actors are doing too little to address climate change. Republicans are much more likely to say most of these groups are doing about the right amount than to say they are doing too much to address climate change.
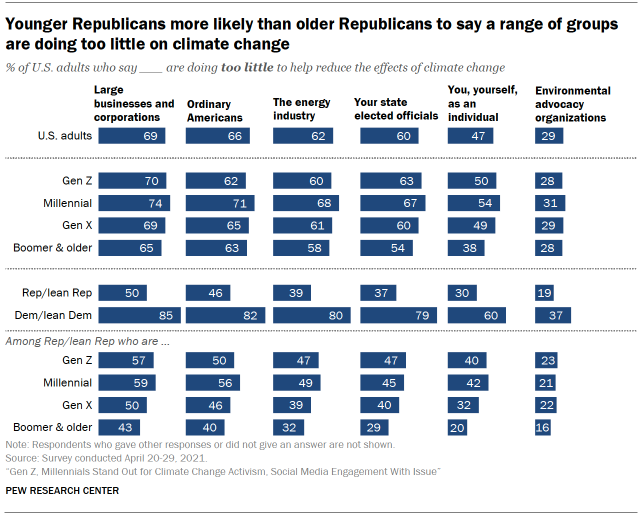
Generational differences in views are most pronounced on this question within the GOP. In general, Gen Z and Millennial Republicans are more likely than older Republicans to say groups and individuals are doing too little to help reduce the effects of climate change. For instance, 57% of Gen Z and 59% of Millennial Republicans say large businesses are doing too little to help address climate change, compared with 50% of Gen X Republicans and 43% of Baby Boomer and older Republicans.
A 54% majority of U.S. adults see climate scientists’ role on policy as too limited, though some have doubts about scientists’ understanding
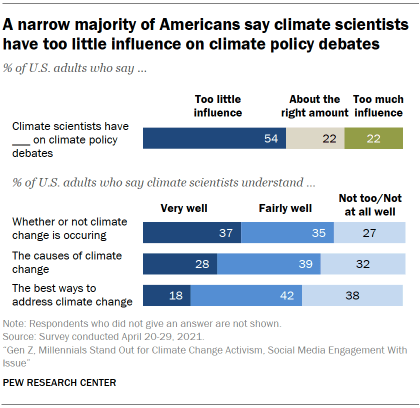
As the Biden administration, Congress and state and local governments debate how best to address climate change, 54% of Americans think climate scientists have too little influence on policy debates about climate change. Smaller shares say climate scientists have about the right amount (22%) or too much (22%) influence on climate policy.
At the same time, Americans appear to have reservations about climate scientists’ expertise and understanding. Only about two-in-ten Americans (18%) say climate scientists understand “very well” the best ways to address climate change. Another 42% say climate scientists understand ways to address climate change “fairly well”; 38% say they understand this not too or not at all well.
Public views of climate scientists’ understanding are more positive, if still generally skeptical, on the fundamentals of whether climate change is occurring (37% say scientists understand this very well) and what causes climate change (28%).
Americans’ overall views about climate scientists’ expertise and understanding of what is happening to the Earth’s climate are similar to 2016, the last time Pew Research Center asked these questions.
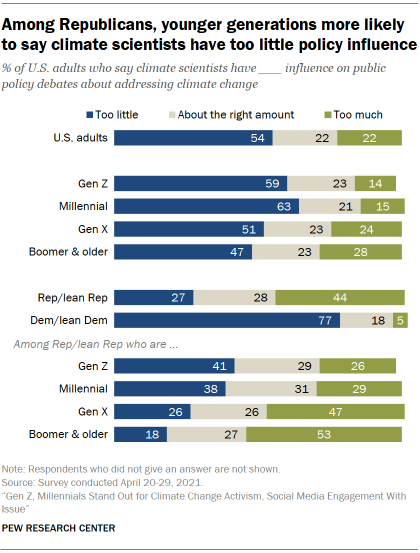
In keeping with the wide political divisions over climate policy issues, Democrats are far more likely than Republicans to rate climate scientists’ understanding highly. And these partisan divides have widened since 2016. For example, Democrats are 43 percentage points more likely than Republicans to say climate scientists understand very well whether or not climate change is occurring. This gap was 25 points in 2016. See the Appendix for details.
Similarly, far larger shares of Democrats than Republicans believe climate scientists have too little say in climate debates (77% vs. 27%).
Younger generations are especially likely to think climate scientists have too little say on climate policy debates. However, these generational dynamics occur only within the GOP.
Millennial (38%) and Gen Z (41%) Republicans are more likely than Baby Boomers and older generations of Republicans (18%) to think climate scientists have too little influence on related policy debates. About half of older Republicans (53%) say climate scientists have too much influence in these debates.
Roughly three-quarters to eight-in-ten Democrats across younger and older generations think climate scientists have too little say in climate policy debates.
Majority of Americans continue to say federal government is doing too little to protect key aspects of the environment
When it comes to environmental protection, a majority of Americans continue to see a role for stricter environmental regulations and majorities view the federal government as doing too little across most areas of environmental concern asked about in the survey, such as protecting air quality.
Gen Z and Millennials offer the broadest support for environmental regulations and for more government action to protect specific aspects of the environment.
Partisan gaps over government action to protect the environment remain very large and differences over the value of stricter environmental regulations have widened since last asked in September 2019 during the administration of Donald Trump.
There are generational and partisan differences over value of environmental regulations
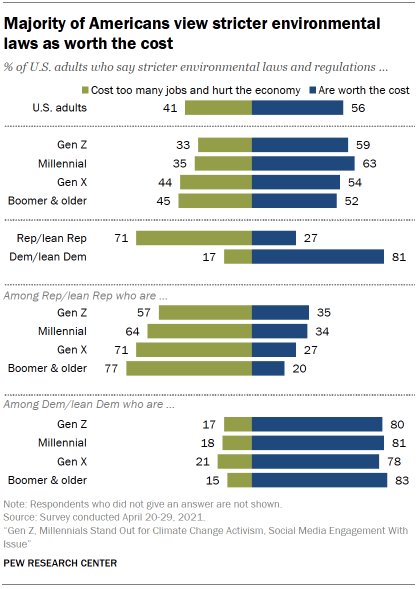
Overall, 56% of Americans say that stricter environmental laws are worth the cost, compared with a smaller share (41%) who say they cost too many jobs and hurt the economy.
On balance Gen Z and Millennials are both much more likely to stricter environmental laws as worth the cost than to say they cost too many jobs and hurt the economy (by 59% to 33% and 63% to 35%, respectively). Gen X and Boomer and older adults also see stricter environmental laws as worth the cost, though by narrower margins.
A large majority of Democrats (81%) believe that stricter environmental laws are worth the cost. By contrast, 71% of Republicans say they cost too many jobs and hurt the economy. Republicans have become much more likely to take a critical view of stricter environmental regulations since September 2019, when 55% said they hurt the economy and cost too many jobs. (For more details on this change over time, see the Appendix).
Generational differences in views occur primarily within the GOP and not among Democrats. Among Republicans, Gen Z (35%) and Millennials (34%) are more likely than Baby Boomer and older adults (20%) to say stricter environmental laws are worth the cost, though larger shares across cohorts say these regulations cost too many jobs and hurt the economy. Roughly eight-in-ten Democrats across generations say that stricter environmental laws are worth the cost.
Far more Americans say government is doing too little, rather than too much, on key areas of environmental protection
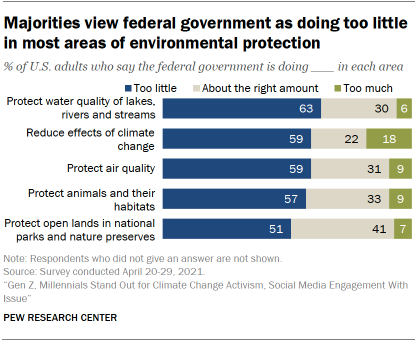
Consistent with Center surveys over the past few years, majorities of U.S. adults support more government action to address a range of environmental concerns, including air and water quality as well as climate change.
Overall, 63% say the federal government is doing too little to protect the water quality of lakes, rivers and streams. Majorities also say the government is doing too little to reduce the effects of climate change (59%), protect air quality (59%) and protect animals and their habitats (57%). About half (51%) say the federal government is doing too little to protect open lands in national parks and nature preserves. Across all five items, small shares of the public believe the government is doing too much to address any one of these environmental issues.
There are wide differences in views on these issues by political party, with Democrats much more likely than Republicans to think that government efforts in these areas are insufficient.
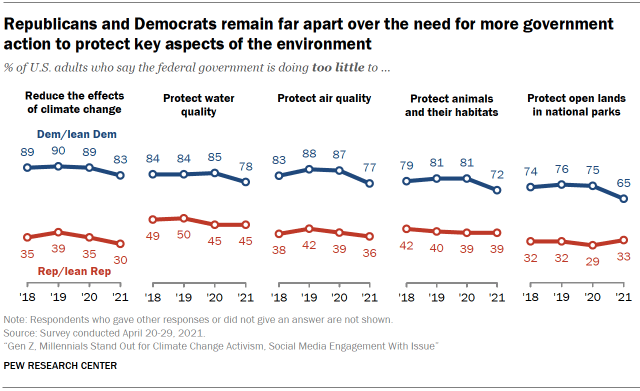
While still the predominant viewpoint, the shares of Democrats who say the government is doing too little across these five areas are 6 to 10 percentage points lower than they were in May of 2020, before Joe Biden took office. Republicans’ views on these questions have been largely steady, although the share of Republicans who believe the federal government is doing too little to address climate change is down 5 percentage points, from 35% in May 2020 to 30% today.
Partisan groups remain far apart when it comes to assessment of government action on climate change: 83% of Democrats and Democratic leaners think the government’s efforts are insufficient, vs. 30% of Republicans and GOP leaners, a difference of 53 percentage points. Conservative Republicans stand out on this from their fellow partisans with a moderate or liberal ideology: 19% say the federal government is doing too little to address climate change compared with 49% of moderate or liberal Republicans.
Gen Zers and Millennials are more likely than older Americans to say the government is doing too little to address specific areas of environmental concern, though these divides are driven primarily by differences by generation within the GOP.
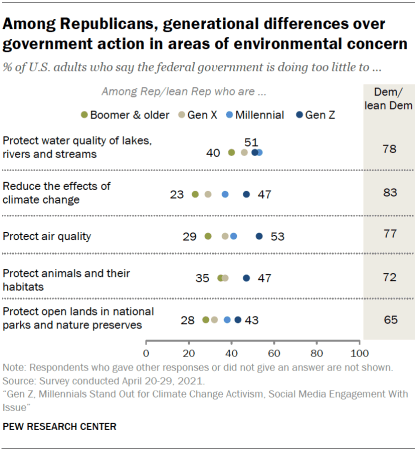
About two-thirds of Gen Zers (66%) and Millennials (65%) say the federal government is doing too little to protect air quality, compared with 58% of Gen X and 52% of Baby Boomer and older adults.
Similarly, 68% of Gen Zers and 66% of Millennials say the federal government is doing too little to reduce the effects of climate change versus 57% of Gen X and 52% of Baby Boomer and older adults.
Among Republicans, Gen Zers and Millennials are more likely than Baby Boomer and older adults to say the federal government is doing too little to address all five of these areas of environmental concern. Majorities of Democrats across generations say the government is doing too little to address these environmental issues.




