This roundup of findings shows public views about science-related issues and the role of science in Japanese society. The findings come from a Pew Research Center survey conducted across 20 publics in Europe, the Asia-Pacific, Russia, the U.S., Canada and Brazil from October 2019 to March 2020.

Ratings of medical treatments, scientific achievements and STEM education in Japan
Majorities in most of the 20 publics surveyed saw their medical treatments in a favorable light on the eve of the global pandemic. Medical treatments were often seen more favorably than achievements in other areas.
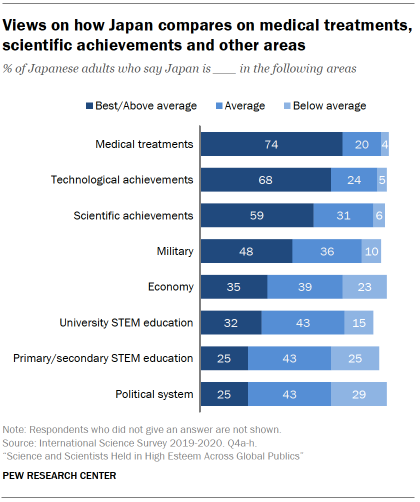
Across the 20 publics, a median of 59% say their medical treatments are at least above average. In Japan, views are more positive: 74% think their country’s medical treatments are the best in the world or above average. Only 4% of Japanese adults think their medical treatments are below average.
About seven-in-ten Japanese adults say their technological achievements are at least above average (68%), and roughly six-in-ten say their scientific achievements are at least above average (59%). By contrast, relatively few think Japan’s university STEM education (32%) or primary and secondary STEM education (25%) are the best in the world or above average.
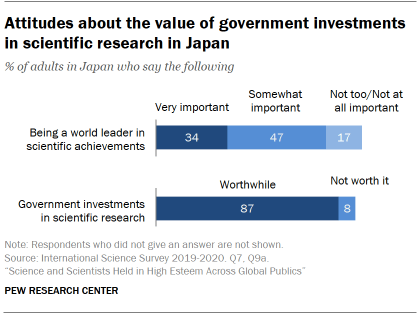
Majorities in all publics agree that being a world leader in scientific achievement is at least somewhat important, but the share who view this as very important varies by public. A 20-public median of 51% place the highest level of importance on being a science world leader. In Japan, only 34% say being a world leader in scientific achievements is very important.
Overall, there is broad agreement among these 20 publics that government investment in scientific research is worthwhile. A median of 82% say government investments in scientific research aimed at advancing knowledge are usually worthwhile for society over time. In Japan, 87% of people say this.
Views on artificial intelligence, food science and childhood vaccines in Japan
Majorities in most publics see their government’s space exploration program as a good thing for society. Across the 20 publics, a median of 72% say their government’s space exploration program has mostly been a good thing for society. In Japan, 84% say the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency’s space exploration program has been good for society.
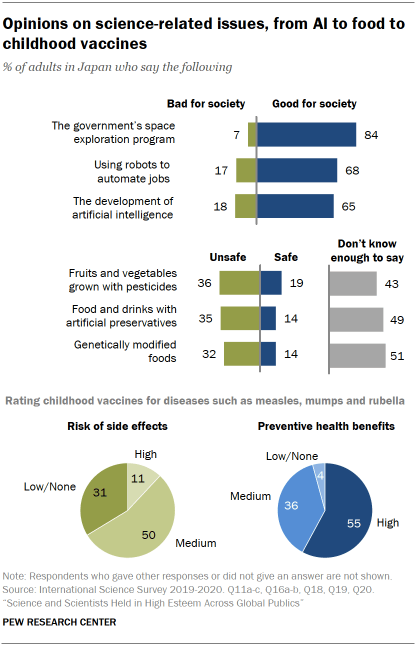
Public views on artificial intelligence (AI) and using robots to automate jobs are more varied from public to public. A median of 53% say the development of AI, or computer systems designed to imitate human behaviors, has mostly been a good thing for society, while 33% say it has been a bad thing. The Center survey also finds that publics offer mixed views about the use of robots to automate jobs. Across the 20 publics, a median of 48% say such automation has mostly been a good thing, while 42% say it has been a bad thing.
In Japan, people have more positive views of both developments. About two-thirds (65%) say artificial intelligence has been good for society, while 18% say it has been bad. A comparable majority (68%) says workplace automation through robotics has been a positive development.
Across most of the publics surveyed, views about the safety of fruits and vegetables grown with pesticides, food and drinks with artificial preservatives and genetically modified foods tilt far more negative than positive. About half think produce grown with pesticides (median of 53%), foods made with artificial preservatives (53%) or genetically modified foods (48%) are unsafe. In Japan, 19% say fruits and vegetables grown with pesticides are safe, while 36% think they are unsafe, and 43% say they don’t know enough about this issue to say. More also view genetically modified foods and food and drinks with artificial preservatives as more unsafe than safe, though about half say they don’t know enough about this issue to say.
When it comes to childhood vaccines such as the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine, a median of 61% say the preventive health benefits of such vaccines are high, and a median of 55% think there is no or only a low risk of side effects. Overall, 55% of Japanese adults say the preventive health benefits from the MMR vaccine are high. However, a comparatively small share (31%) views the risk of side effects from the MMR vaccine as low or none.

Opinions on environmental protection and how much the national government is doing on climate change
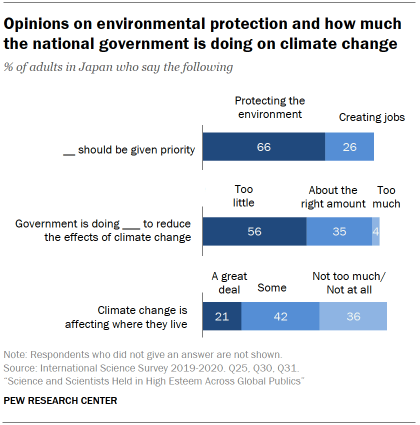
Majorities across all 20 survey publics would prioritize protecting the environment, even if it causes slower economic growth. A median of 71% would prioritize environmental protection. In Japan, about two-thirds (66%) think protecting the environment should be given priority, even if it causes slower economic growth and some loss of jobs. A smaller share (26%) thinks creating jobs should be the top priority, even if the environment suffers to some extent.
Public concern about global climate change has gone up over the past few years in many publics surveyed by the Center.
Majorities in all 20 publics say they are seeing at least some effects of climate change where they live. A median of 70% say they are experiencing a great deal or some effects of climate change where they live. In Japan, about six-in-ten (63%) say climate change is affecting where they live a great deal (21%) or some (42%).
A 20-public median of 58% say their national government is doing too little to reduce the effects of climate change. A majority of 56% in Japan say their government is doing too little to reduce the effects of climate change, while 35% say the government is doing about the right amount, and just 4% say it is doing too much.
Find out more
Read the full report online.
All surveys were conducted with nationally representative samples of adults ages 18 and older. Here is the survey methodology used in each public.