
New York Gov. Kathy Hochul recently announced that she will introduce legislation to ban smartphones in schools during her state’s 2025 legislative session. She cited the impact that social media and technology can have on youth, including leaving them “cut off from human connection, social interaction and normal classroom activity.”
Hochul’s legislative push comes as K-12 teachers in the United States face challenges around students’ cellphone use, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in fall 2023. One-third of public K-12 teachers say students being distracted by cellphones is a major problem in their classroom, and another 20% say it’s a minor problem.
Following news that New York Gov. Kathy Hochul is seeking to ban smartphones in schools, Pew Research Center published this analysis to examine how K-12 teachers and teens in the United States feel about cellphones, including the use of cellphones at school.
This analysis is based on two recent Center surveys, one of public K-12 teachers in the U.S. and the other of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17. More information about these surveys, including their field dates, sample sizes and other methodological details, is available at the links in the text.
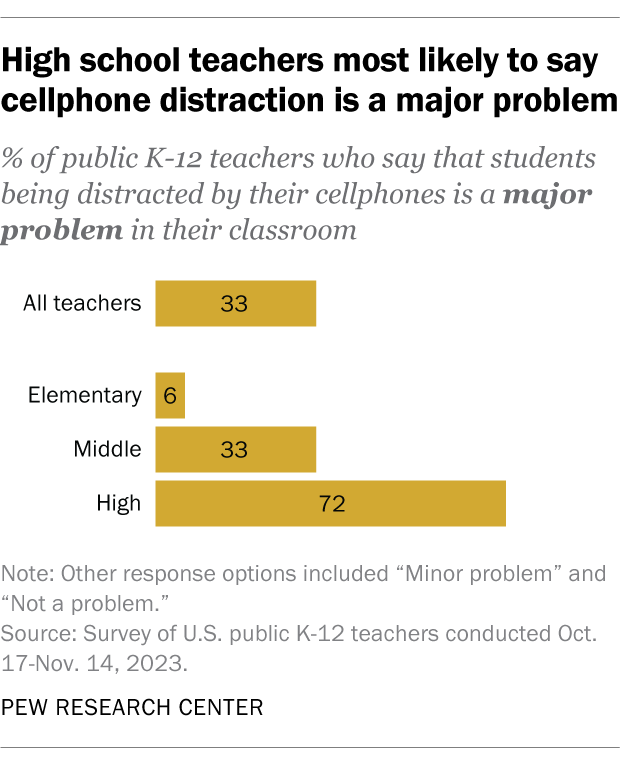
High school teachers are especially likely to see cellphones as problematic. About seven-in-ten (72%) say that students being distracted by cellphones is a major problem in their classroom, compared with 33% of middle school teachers and 6% of elementary school teachers.
Many schools and districts have tried to address this challenge by implementing cellphone policies, such as requiring students to turn off their phones during class or give them to administrators during the school day.
Overall, 82% of K-12 teachers in the U.S. say their school or district has a cellphone policy of some kind. Middle school teachers (94%) are especially likely to say this, followed by elementary (84%) and high school (71%) teachers.
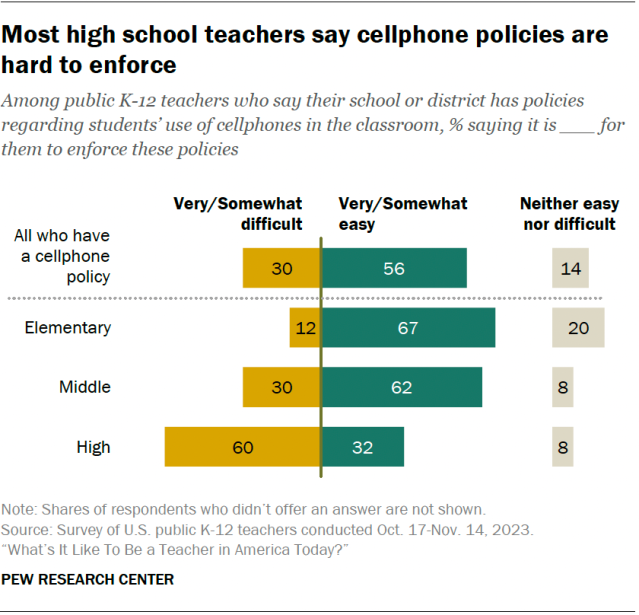
However, 30% of teachers whose schools or districts have cellphone policies say they are very or somewhat difficult to enforce. High school teachers are more likely than their peers to report that enforcing these policies is difficult. Six-in-ten high school teachers in places with a cellphone policy say this, compared with 30% of middle school teachers and 12% of elementary school teachers.
Our survey asked teachers about cellphones in general, whereas Hochul’s plan would apply only to smartphones. Even so, nearly all U.S. teenagers ages 13 to 17 – 95% – say they have access to a smartphone, according to a separate Center survey from 2023.
Even as some policymakers and teachers see downsides to smartphones, teens tend to view the devices as a more positive than negative thing in their lives overall.
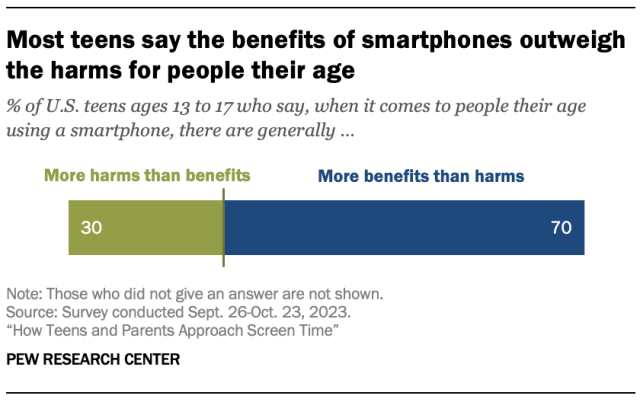
Seven-in-ten teens ages 13 to 17 say there are generally more benefits than harms to people their age using smartphones, while three-in-ten say the opposite. And 45% of teens say smartphones make it easier for people their age to do well in school, compared with 23% who say they make it harder. Another 30% say smartphones don’t affect teens’ success in school.
