
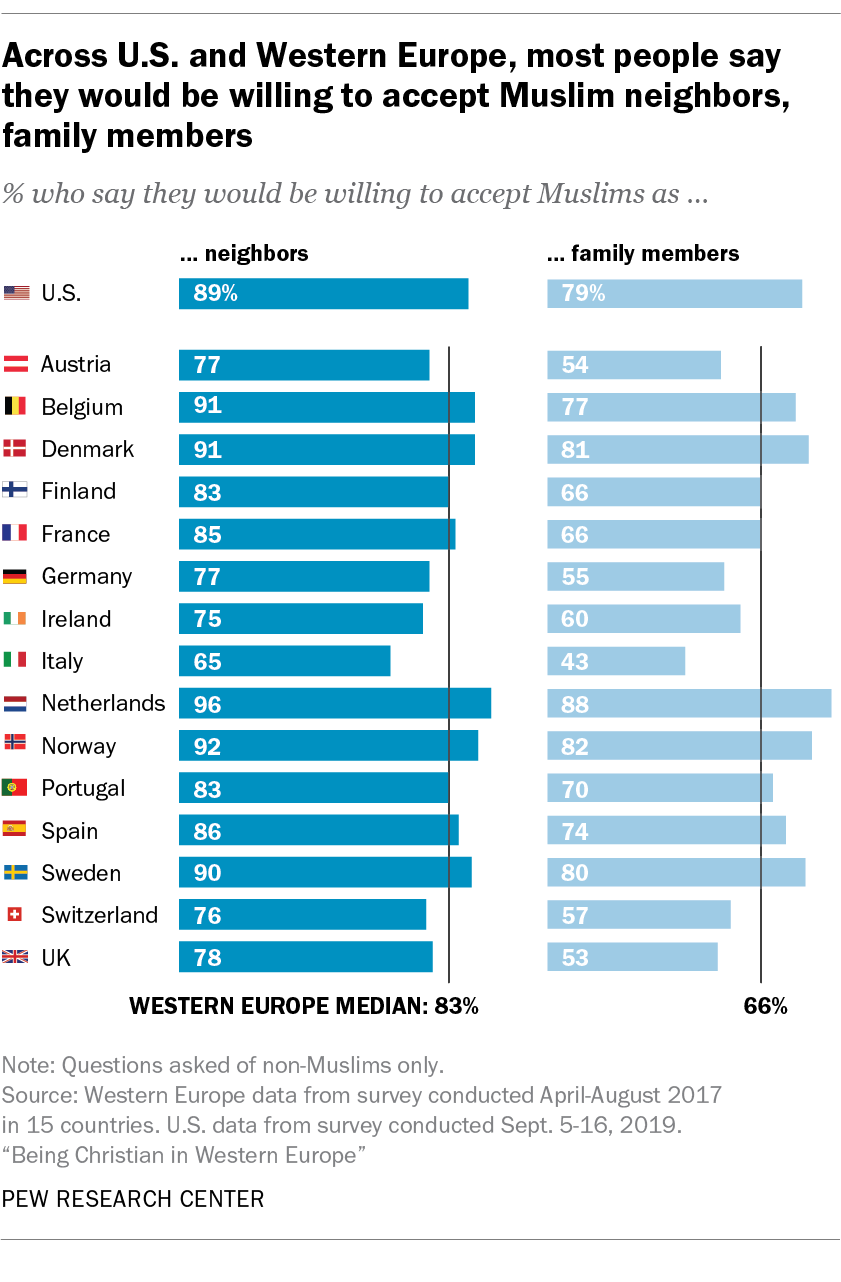
The vast majority of people across 15 countries in Western Europe and in the United States say they would be willing to accept Muslims as neighbors. Slightly lower shares on both sides of the Atlantic say they would be willing to accept a Muslim as a family member.
At the same time, there is no consensus on whether Islam fits into these societies. Across Western Europe, people are split on Islam’s compatibility with their country’s culture and values, according to a 2017 Pew Research Center survey. And in the U.S., public opinion remains about evenly divided on whether Islam is part of mainstream American society and if Islam is compatible with democracy, according to a 2017 poll.
The vast majority of non-Muslim Americans (89%) say they would be willing to accept Muslims as neighbors, according to a new Pew Research Center survey. The same survey finds that most people (79%) say they would be willing to accept Muslims as members of their family.
In Western Europe, most people also say they would be willing to accept Muslim neighbors. However, Europeans are less likely than Americans to say they would be willing to accept Muslims as family members. While about two-thirds of non-Muslim French people (66%) say they would accept a Muslim in their family, just over half of British (53%), Austrian (54%) and German (55%) adults say this. Italians are the least likely in Europe to say they would be willing to accept a Muslim family member (43%).
Surveys in both the U.S. and Western Europe were conducted on the telephone, and due to the tendency of some respondents to give socially acceptable responses, may overstate the share of people willing to accept others (also known as social desirability bias).
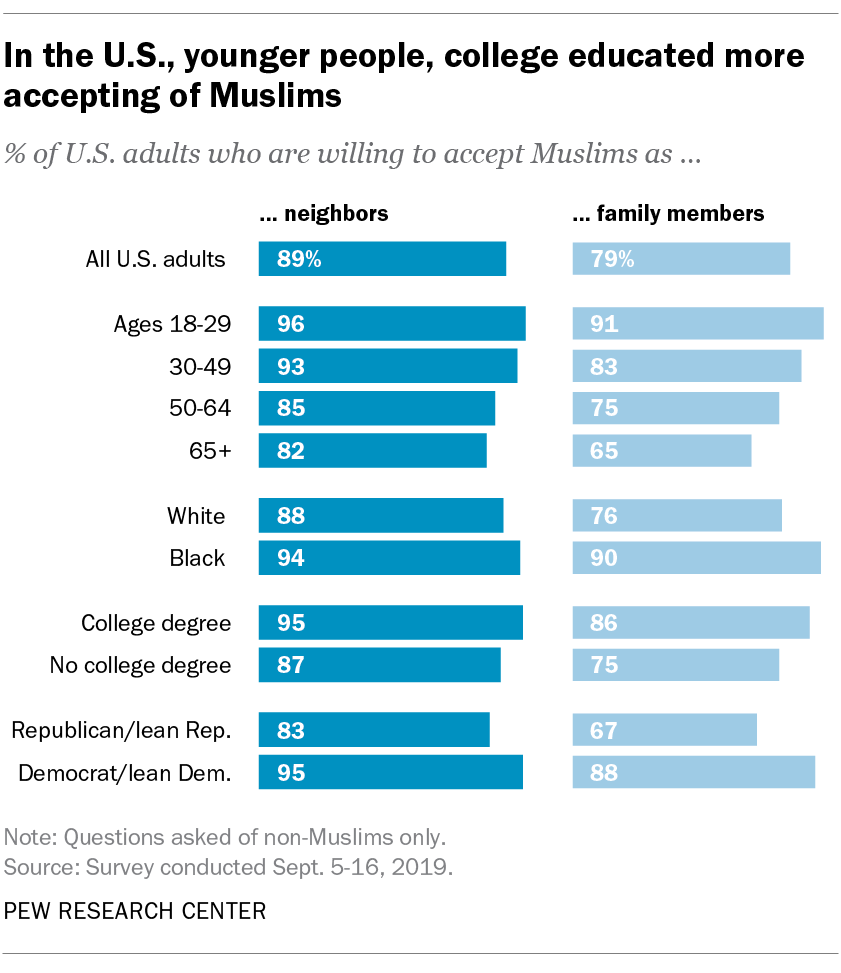
In both the U.S. and Europe, the surveys find higher acceptance of Muslims among those with more education. In the U.S., for example, 86% of adults with a college degree would be willing to accept a Muslim into their family; among Americans without a college degree, this share falls to 75%. Similarly, in Germany, a majority of those with a college education (67%) say they would be willing to accept a Muslim in their family, compared with roughly half (52%) among those without one. The same pattern is present in other countries, such as the UK (71% vs. 44%) and Austria (67% vs. 51%).
On both sides of the Atlantic, attitudes toward Muslims are tied to politics, even after taking education, age and other demographic factors into account. In Western Europe, those who lean toward the right of the European political spectrum have less accepting views than those who lean toward the left. Likewise, in the U.S., those who identify with or lean toward the Democratic Party are more likely than Republicans and Republican leaners to say they would be willing to accept a Muslim family member (88% vs. 67%). Still, majorities among both Democrats and Republicans say they would be willing to accept Muslims in their lives. Additional analysis of how other demographic factors (such as religion) are correlated with these kinds of attitudes in Europe can be found here.
[their country’s]
Pew Research Center has not asked this exact question in the U.S. Still, several other survey questions point to a similar ambivalence in American public opinion about the role of Islam in society. For instance, half of American adults say Islam is not part of mainstream American society and a similar share (44%) say there is a natural conflict between Islam and democracy.
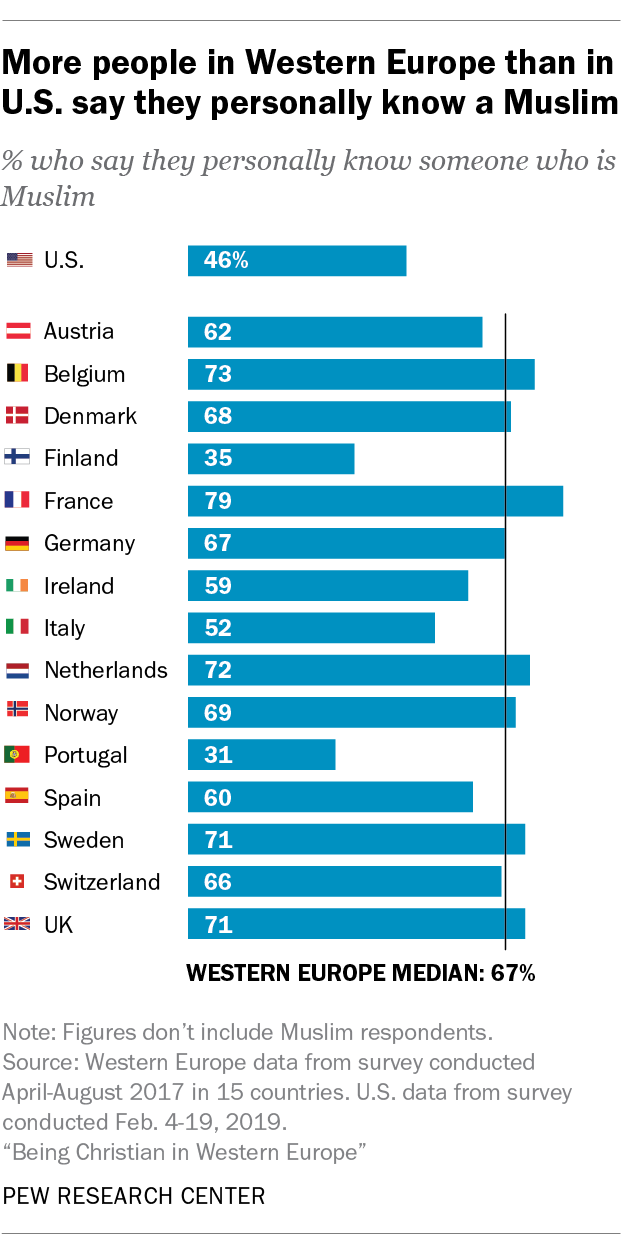
Muslims make up roughly 1% of the adult population in the U.S., while across Europe as a whole (including Eastern Europe), they are estimated to form roughly 5% of the population, including 6% in the UK and Germany, and nearly 9% in France. Also, 46% of American adults say they personally know a Muslim, compared with significant majorities in most Western European countries, including 71% in the UK and 79% in France.

