More coverage
- Report: The Growing Diversity of Black America
- Statistical portraits: Facts about the U.S. Black population
- Detailed tables
The Black population in the United States is diverse and growing. A new Pew Research Center analysis of U.S. Census Bureau data explores the demographic characteristics of this population in 2019. Here are key findings from this analysis. A full statistical portrait of the Black population can be found in this fact sheet. To learn how we defined this population and subgroups, visit the terminology section.
This analysis of the Black population in the United States uses the latest demographic data available. It is based on data from the U.S. Census Bureau’s 2019 American Community Survey, provided through the Integrated Public Use Microdata Series (IPUMS) from the University of Minnesota.
This analysis relies on self-identification of race and ethnicity in U.S. Census Bureau products (decennial censuses and iterations of the American Community Survey) to identify the nation’s Black population. However, an individual’s racial and ethnic self-identification may not be fixed and instead can change over time. In addition, the racial and ethnic categories used by the U.S. Census Bureau can change as the way the nation sees itself changes. These changes may impact how many people identify as Black (or any other race). The full methodology can be found here.
The Black population is growing. There were 46.8 million people in the U.S. who identified as Black in 2019. The Black population has grown by more than 10 million since 2000, when 36.2 million of the country’s population identified as Black, a 29% increase over almost two decades. This population growth rate is larger than that of the White population over the same time span (13%) but less than that of the Asian and Hispanic U.S. populations (89% and 72%, respectively).
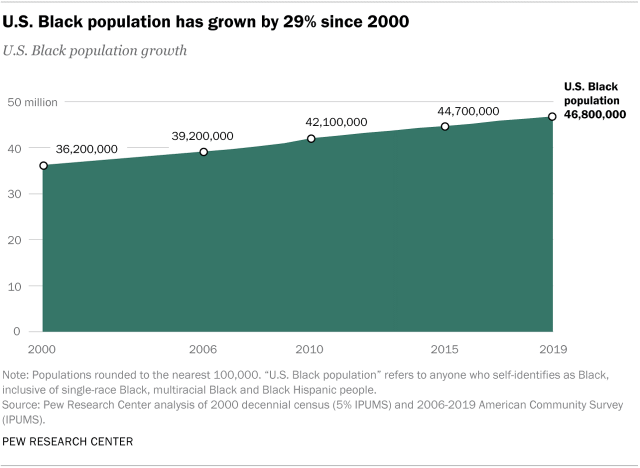
Black population growth stems from both those born in the U.S. and those born abroad. While 90% of the U.S. Black population was born in the U.S. – a number that has risen by 25% since 2000 – there has been a more dramatic increase among the foreign-born population. More than 4.6 million Black people in the U.S. were born outside the country as of 2019, meaning that 10% of the Black population was foreign born. This is an increase of nearly 90% from 2000, when the foreign-born population stood at 2.4 million, or 7% of the overall U.S. Black population. Most Black immigrants (88%) were born in African or Caribbean nations.
The Black population is getting more diverse as it grows. Among those who self-identify on census forms as “Black or African American,” the share who say it is their only racial or ethnic identification has slightly declined over the past two decades. In 2019, 40.7 million, or 87%, identified their race as Black alone and their ethnicity as non-Hispanic, while around 3.7 million, or 8%, indicated their race was Black and another race (most often White) and not Hispanic. Another 2.4 million, or 5%, self-identified as both Black and Hispanic, or Black Hispanic (though not all Black Hispanics identify as Afro-Latino). These shares have changed since 2000, when 93% identified their race and ethnicity as Black alone.

The Black population is relatively young. As of 2019, the median age of single-race, non-Hispanic Black people is 35, compared with 30 in 2000. This makes the population younger than the nation’s White population (median age of 43) and the Asian population (38), and slightly older than the nation’s Hispanic population (29). (The White and Asian populations are single-race, non-Hispanic.)
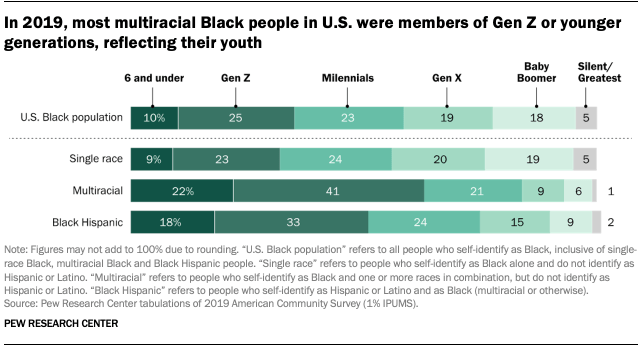
The Black population is slightly younger when including those who identify with more than one racial or ethnic group. The median age for the total U.S. Black population is 32, though it varies across various identities among the Black population. Among Black Hispanic people, the median age is 22 years. Meanwhile, non-Hispanic multiracial Black people are the youngest group, with a median age of 16.
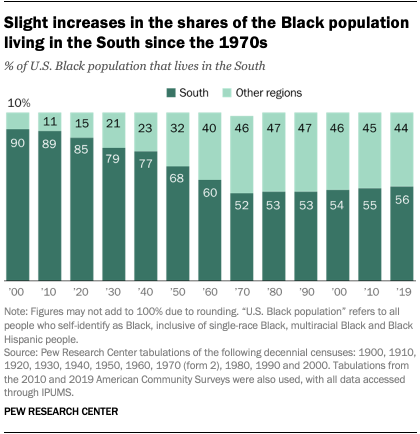
Just over half of all Black people in the U.S. live in the South, a share that has risen some in recent decades. The growth of the Black population in the South suggests a departure from previous Black migration patterns. After the start of the Great Migration in the late 1910s, growing shares of the Black population lived in regions of the U.S. outside of the South. But after 1970, the share of this population that lived in the South started to grow, a trend that continues today.
Overall, there was a 4 percentage point increase in the share of the Black population that lives in the South between 1970 (52%) and 2019 (56%).
A growing share of Black adults have a college degree. The number of Black adults with a bachelor’s degree or more education has more than doubled since 2000. Roughly 3 million Black adults ages 25 and older, or 15%, had earned at least a bachelor’s degree in 2000, and these numbers grew to 6.7 million (23%) in 2019.
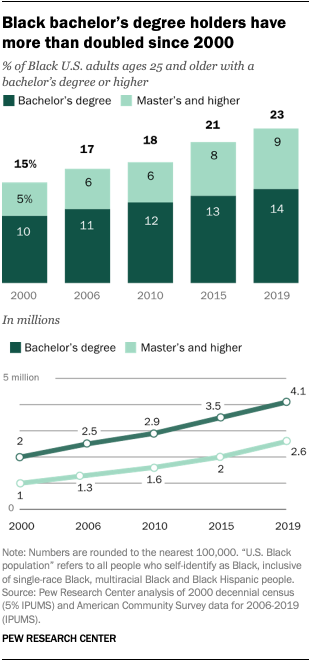
Notably, the share of the Black population with at least a bachelor’s degree has risen at a similar rate to that of the general population. In 2000, roughly a quarter (24%) of the entire U.S. population ages 25 and older had a bachelor’s degree or higher. In 2019, that share rose to 33%, an increase of 9 points. The share of Black adults who earned a bachelor’s degree or higher also grew nearly 9 points during this time, from 15% to 23%.
There has been a similar upward trend among Black adults 25 and older with a master’s degree or higher. While roughly 1 million (5% of Black adults) had an advanced degree in 2000, that number rose to almost 2.6 million, or 9%, in 2019.
When it comes to different subgroups of the Black population, the multiracial Black population has the highest shares of adults 25 and older with a bachelor’s degree (20%) and advanced degree (12%). Single-race Black adults and Black Hispanics have slightly lower shares of individuals with a bachelor’s degree (14% and 15%, respectively) and with an advanced degree (9% and 8%).
The share of Black adults 25 and older without a high school diploma or equivalent has dropped by more than half since 2000 – from 28% of Black adults in this age group without a diploma in 2000 to 13% in 2019, a 15-point drop over almost two decades.
Note: Here is the methodology for this report.
CORRECTION (March 2, 2023): A previous version of the chart “Among the U.S. Black population, both multiracial and Hispanic numbers have grown sharply since 2000” displayed incorrect estimates for the total Black and multiracial Black populations in the U.S. for 2010. None of the study findings or conclusions are affected.