The American Trends Panel (ATP), created by Pew Research Center, is a nationally representative panel of randomly selected U.S. adults. Panelists participate via self-administered web surveys. Panelists who do not have internet access at home are provided with a tablet and wireless internet connection. The panel is being managed by Ipsos.
Data in this report is drawn from the panel wave conducted July 13 to July 19, 2020. A total of 10,211 panelists responded out of 12,981 who were sampled, for a response rate of 79%. No panelists were removed from the data due to extremely high rates of refusal or straightlining. The cumulative response rate accounting for nonresponse to the recruitment surveys and attrition is 4.3%. The break-off rate among panelists who logged on to the survey and completed at least one item is 1%. The margin of sampling error for the full sample of 10,211 respondents is plus or minus 1.5 percentage points.
This study featured a stratified random sample from the ATP. The sample was allocated according to the following strata, in order: tablet households, Mexican-born Hispanics, U.S.-born Hispanics, other foreign-born Hispanics, Cuban-born Hispanics, non-internet, high school education or less, not registered to vote, nonvolunteers, people ages 18 to 34, non-Hispanic Black adults, and all other categories not already falling into any of the above.
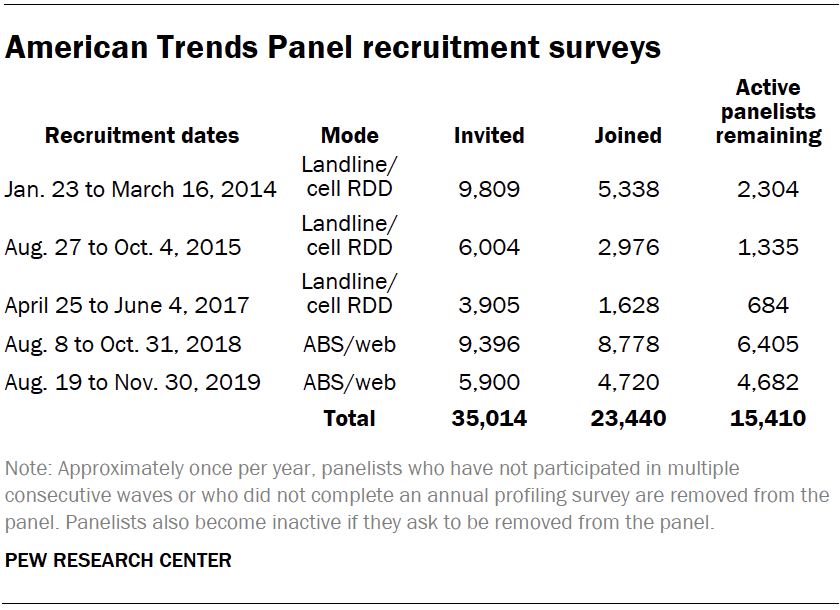
The ATP was created in 2014, with the first cohort of panelists invited to join the panel at the end of a large, national, landline and cellphone random-digit-dial survey that was conducted in both English and Spanish. Two additional recruitments were conducted using the same method in 2015 and 2017, respectively. Across these three surveys, a total of 19,718 adults were invited to join the ATP, of which 9,942 agreed to participate.
In August 2018, the ATP switched from telephone to address-based recruitment. Invitations were sent to a random, address-based sample of households selected from the U.S. Postal Service’s Delivery Sequence File. In each household, the adult with the next birthday was asked to go online to complete a survey, at the end of which they were invited to join the panel. For a random half-sample of invitations, households without internet access were instructed to return a postcard. These households were contacted by telephone and sent a tablet if they agreed to participate. A total of 9,396 were invited to join the panel, and 8,778 agreed to join the panel and completed an initial profile survey. The same recruitment procedure was carried out on August 19, 2019, from which a total of 5,900 were invited to join the panel and 4,720 agreed to join the panel and completed an initial profile survey. Of the 23,440 individuals who have ever joined the ATP, 15,410 remained active panelists and continued to receive survey invitations at the time this survey was conducted.
The U.S. Postal Service’s Delivery Sequence File has been estimated to cover as much as 98% of the population, although some studies suggest that the coverage could be in the low 90% range.7 The American Trends Panel never uses breakout routers or chains that direct respondents to additional surveys.
Weighting

The ATP data was weighted in a multistep process that begins by calibrating the entire panel so that it aligns with the population benchmarks identified in the accompanying table to create a full-panel weight. For ATP waves in which only a subsample of panelists are invited to participate, a wave-specific base weight is created by adjusting the full-panel weights for subsampled panelists to account for any differential probabilities of selection for the particular panel wave. For waves in which all active panelists are invited to participate, the wave-specific base weight is identical to the full-panel weight. The next step in the weighting uses an iterative technique that aligns the sample to population benchmarks on the dimensions listed in the accompanying table.
Sampling errors and test of statistical significance take into account the effect of weighting. Interviews are conducted in both English and Spanish.
In addition to sampling error, one should bear in mind that question wording and practical difficulties in conducting surveys can introduce error or bias into the findings of opinion polls.
The following table shows the unweighted sample sizes and the error attributable to sampling that would be expected at the 95% level of confidence for different groups in the survey:
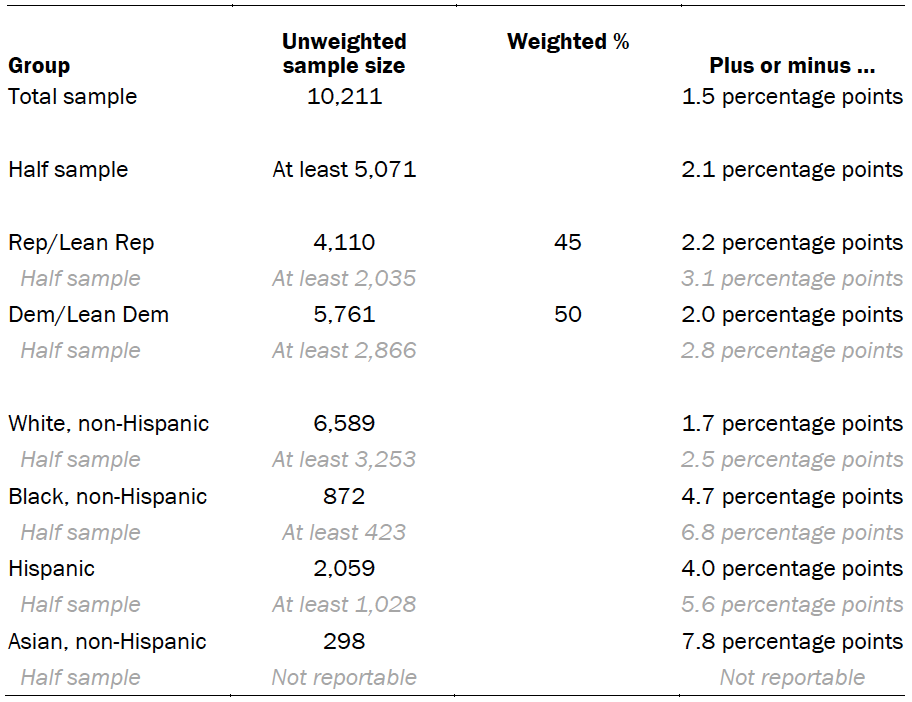
Sample sizes and sampling errors for other subgroups are available upon request. White, Black and Asian adults include those who report being only one race and are non-Hispanic. Hispanics are of any race. Asian adults were interviewed in English only.
A note about the Asian American sample
This survey includes a total sample size of 298 Asian Americans. The sample includes English-speaking Asian Americans only and, therefore, may not be representative of the overall Asian American population (75% of our weighted Asian American sample was born in another country, compared with 77% of the Asian American adult population overall). Despite this limitation, it is important to report the views of Asian Americans on the topics in this study. As always, Asian Americans’ responses are incorporated into the general population figures throughout this report. Asian Americans are shown as a separate group when the question was asked of the full sample. Because of the relatively small sample size and a reduction in precision due to weighting, results are not shown separately for Asian Americans for questions that were only asked of a random half of respondents (Form 1/Form 2) or some filtered questions. We are also not able to analyze Asian American respondents by demographic categories, such as gender, age or education.
Defining income tiers
To create upper-, middle- and lower-income tiers, respondents’ 2018 family incomes were adjusted for differences in purchasing power by geographic region and for household size. “Middle-income” adults live in families with annual incomes that are two-thirds to double the median family income in the panel (after incomes have been adjusted for the local cost of living and for household size). The middle-income range for the American Trends Panel is about $37,500 to $112,600 annually for a three-person household. Lower-income families have incomes less than roughly $37,500, and upper-income families have incomes greater than roughly $112,600.
Based on these adjustments, among respondents who provided their income and household size, 32% are lower income, 43% are middle income and 20% fall into the upper-income tier.
For more information about how the income tiers were determined, please see here.




