U.S. immigration from Latin America has shifted over the past two decades. From 1965 to 2015, more than 16 million Mexicans migrated to the U.S. in one of the largest mass migrations in modern history. But over the past decade, Mexican migration to the U.S. has slowed dramatically. Today, Mexico increasingly serves as a land bridge for Central American immigrants traveling to the U.S.
Here are five facts about Mexico and trends in immigration to the U.S.
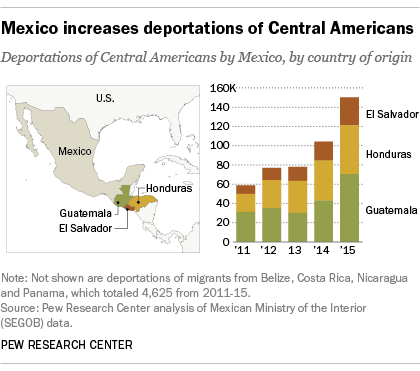
Mexico is stopping more unauthorized Central American immigrants at its southern border. The Mexican government said in 2014 that it would increase enforcement at its southern border in response to an increased flow of Central Americans traveling through Mexico to reach the U.S. In 2015, the government there carried out about 150,000 deportations of unauthorized immigrants from El Salvador, Guatemala and Honduras, a 44% jump over the previous year. These three Central American countries alone accounted for nearly all (97%) of Mexico’s deportations in 2015.
Despite increased enforcement by Mexico, many unauthorized Central Americans are still reaching the U.S. via Mexico. At the U.S.-Mexico border, the number of families and unaccompanied children apprehended by U.S. Customs and Border Protection officials is again rising, though it’s too early to tell how 2016 will compare with prior years. From Oct. 1, 2015, to Jan. 31, 2016, 24,616 families and 20,455 unaccompanied children – the vast majority of them from Central America – were apprehended at the southwestern U.S. border, double the total from the same time period the year before. Apprehensions of unaccompanied children rose to record levels in fiscal 2014, then decreased by 42% in fiscal 2015.
More Cubans are also traveling through Mexico to reach the U.S. The number of Cubans migrating through Mexico to reach the U.S. spiked dramatically last year after President Barack Obama said the U.S. would renew ties with the island nation. In fiscal 2015, 43,159 Cubans entered the U.S. via ports of entry, a 78% increase over the previous year. Two-thirds of these Cubans arrived through the U.S. Border Patrol’s Laredo Sector in Texas. (Cubans who pass an inspection can enter the U.S. legally under the Cuban Adjustment Act of 1966.)
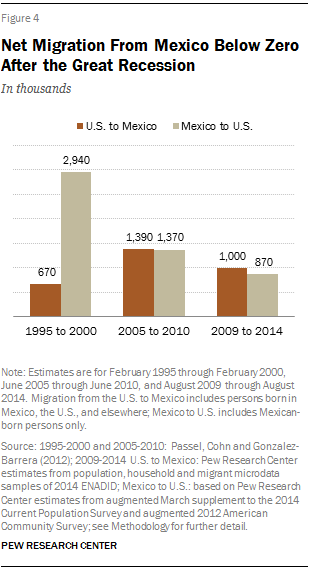
Fewer Mexicans are migrating to the U.S. today than in the past. In fact, more Mexicans left than came to the U.S since the end of the Great Recession. Between 2009 and 2014, 870,000 Mexican nationals left Mexico to come to the U.S., down from the 2.9 million who left Mexico for the U.S. between 1995 and 2000. Of those moving back to Mexico, many cite family as the reason for their return. About 1 million Mexican immigrants and their U.S.-born children moved from the U.S. to Mexico between 2009 and 2014, and 61% said they had done so to reunite with family or to start a family, according to the 2014 Mexican National Survey of Demographic Dynamics.
More Mexicans now say life is about the same in the U.S. and Mexico. In 2015, 33% of Mexican adults said life in the U.S. is neither better nor worse than life in Mexico, up from 23% who said this in 2007. Still, about half of Mexican adults believe life is better in the U.S. and 35% of Mexicans said they would move to the U.S. if they had the opportunity and means to do so, similar shares as in 2009.
