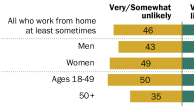Executive Summary
This report is based on findings from a pair of Pew Research Center surveys conducted this spring. One is a telephone survey taken among a nationally representative sample of 2,142 adults ages 18 and older. The other is an online survey, done in association with the Chronicle of Higher Education, among the presidents of 1,055 two-year and four-year private, public, and for-profit colleges and universities. (See a description of our survey methodology.)
Here is a summary of key findings:
Survey of the General Public
- Cost and Value. A majority of Americans (57%) say the higher education system in the United States fails to provide students with good value for the money they and their families spend. An even larger majority—75%—says college is too expensive for most Americans to afford. At the same time, however, an overwhelming majority of college graduates—86%—say that college has been a good investment for them personally.
- Monetary Payoff. Adults who graduated from a four-year college believe that, on average, they are earning $20,000 more a year as a result of having gotten that degree. Adults who did not attend college believe that, on average, they are earning $20,000 a year less as a result. These matched estimates by the public are very close to the median gap in annual earnings between a high school and college graduate as reported by the U.S. Census Bureau in 2010: $19,550. A more detailed Pew Research Center analysis (see Chapter 5) shows that this gap varies by type of degree and field of study.
- Student Loans. A record share of students are leaving college with a substantial debt burden, and among those who do, about half (48%) say that paying off that debt made it harder to pay other bills; a quarter say it has made it harder to buy a home (25%); and about a quarter say it has had an impact on their career choices (24%).
- Why Not College? Nearly every parent surveyed (94%) says they expect their child to attend college, but even as college enrollments have reached record levels, most young adults in this country still do not attend a four-year college. The main barrier is financial. Among adults ages 18 to 34 who are not in school and do not have a bachelor’s degree, two-thirds say a major reason for not continuing their education is the need to support a family. Also, 57% say they would prefer to work and make money; and 48% say they can’t afford to go to college.
- Split Views of College Mission. Just under half of the public (47%) says the main purpose of a college education is to teach work-related skills and knowledge, while 39% say it is to help a student grow personally and intellectually; the remainder volunteer that both missions are equally important. College graduates place more emphasis on intellectual growth; those who are not college graduates place more emphasis on career preparation.
- For Most College Graduates, Missions Accomplished. Among survey respondents who graduated from a four-year college, 74% say their college education was very useful in helping them grow intellectually; 69% say it was very useful in helping them grow and mature as a person; and 55% say it was very useful in helping them prepare for a job or career.
- Above All, Character. While Americans value college, they value character even more. Asked what it takes for a young person to succeed in the world, 61% say a good work ethic is extremely important and 57% say the same about knowing how to get along with people. Just 42% say the same about a college education.
Survey of Presidents
- Right or Wrong Direction? Six-in-ten college presidents say the system of higher education in this country is headed in the right direction, but a substantial minority—38%—say it is headed in the wrong direction.
- Declining Student Quality. A majority of college presidents (58%) say public high school students arrive at college less well prepared than their counterparts of a decade ago; just 6% say they are better prepared. Also, 52% of presidents say college students today study less than their predecessors did a decade ago; just 7% say they study more.
- We’re Not Number One. Only 19% of college presidents say the U.S. system of higher education is the best in the world now, and just 7% say they believe it will be the best in the world ten years from now. Most presidents —51%—describe the U.S. system as one of the best in the world.
- Doubts about Achieving Obama’s Goal. Nearly two-thirds of college presidents (64%) say it is unlikely that, by 2020, the U.S. will achieve the goal set by President Obama to have the highest share of young adults with a college degree or certificate of any country in the world.
- Who Should Pay? Nearly two-thirds of college presidents (63%) say students and their families should pay the largest share of the cost of a college education. Just 48% of the public agrees. An equal share of the public would prefer that the bulk of the cost of a college education be borne by the federal government, state governments, private endowments or some combination.
- Split Views of College Mission. Presidents are evenly divided about the main role colleges play in students’ lives: Half say it is to help them mature and grow intellectually, while 48% say it is to provide skills, knowledge and training to help them succeed in the working world. Most heads of four-year colleges and universities emphasize the former; most heads of two-year and for-profit schools emphasize the latter.
- Measuring Grade Inflation: Just over a quarter (27%) of college presidents say that the faculty at their own institution grades students too leniently. Only 1% says they grade students too stringently. The vast majority (73%) says students are graded about right.
- Scant Enthusiasm for Faculty Tenure. Only a quarter (24%) of presidents say that, if given a choice, they would prefer that most faculty at their institution be tenured. About seven-in-ten say they would prefer that faculty be employed on annual or long term contracts.
About the Surveys
This report is largely based on findings from two Pew Research Center surveys conducted in the spring of 2011.
The general public survey (GP) is based on telephone interviews conducted with a nationally representative sample of 2,142 adults ages 18 and older living in the continental United States, including an oversample of 336 adults ages 18-34. A total of 1,052 interviews were completed with respondents contacted by landline telephone and 1,090 with those contacted on their cellular phone. The data are weighted to produce a final sample that is representative of the general population of adults in the continental United States. Survey interviews were conducted under the direction of Princeton Survey Research Associates International, in English and Spanish. For more details, see Appendix 1.
- Interviews conducted March 15-29, 2011
- 2,142 interviews
- Margin of sampling error is plus or minus 2.7 percentage points for results based on the total sample and 4.5 percentage points for adults 18 to 34 years old at the 95% confidence level.
The college presidents survey (P) is based on a web survey conducted with 1,055 college and university presidents in the U.S. The survey was designed by the Pew Research Center in association with the Chronicle of Higher Education. Overall, 1,022 interviews were completed online and 33 interviews were completed by phone (for the presidents who requested being interviewed by phone). The college and university presidents surveyed are from four major sectors: 1) private four-year colleges and universities; 2) public four-year colleges and universities; 3) two-year public and private colleges; 4) four-year and two-year for-profit colleges and universities. The data were weighted to correct for disproportionate non-response that might bias sample estimates. The weighting accounts for both the institution type and geographic distribution of the colleges and universities eligible to take part in the survey. Survey interviews were conducted in English under the direction of Princeton Survey Research Associates International. For more details, see Appendix 1.
- Interviews conducted March 15-April 24, 2011
- 1,055 interviews
- Margin of error is plus or minus 2.8 percentage points at the 95% confidence level for results based on the total sample, 4.8 percentage points for presidents of four-year public universities, 3.8 percentage points for presidents of four-year private universities, 4.6 percentage points for presidents of two-year colleges (public or private), and 11.3 percentage points for presidents of private for-profit colleges and universities.
Notes on Terminology
Unless otherwise noted, “college graduates” refers to those who graduated from a four-year college and hold a bachelor’s degree or higher.
In referring to institutions of higher education, the terms “school,” “institution,” “college” and “university” are used interchangeably, except that “university” does not apply to two-year institutions.
“Private college” refers to private (as opposed to public) not-for-profit (NFP) colleges and universities. This term is not intended to apply to private, for-profit colleges.