Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand Americans’ attitudes toward and personal experiences with dating and relationships. These findings are based on a survey conducted Oct. 16-28, 2019, among 4,860 U.S. adults. This includes those who took part as members of Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses, as well as respondents from the Ipsos KnowledgePanel who indicated that they identify as lesbian, gay or bisexual (LGB).
Recruiting ATP panelists by phone or mail ensures that nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. This gives us confidence that any sample can represent the whole U.S. adult population (see our Methods 101 explainer on random sampling). To further ensure that each ATP survey reflects a balanced cross-section of the nation, the data are weighted to match the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories.
For more, see the report’s methodology about the project. You can also find the questions asked, and the answers the public provided, in this topline.
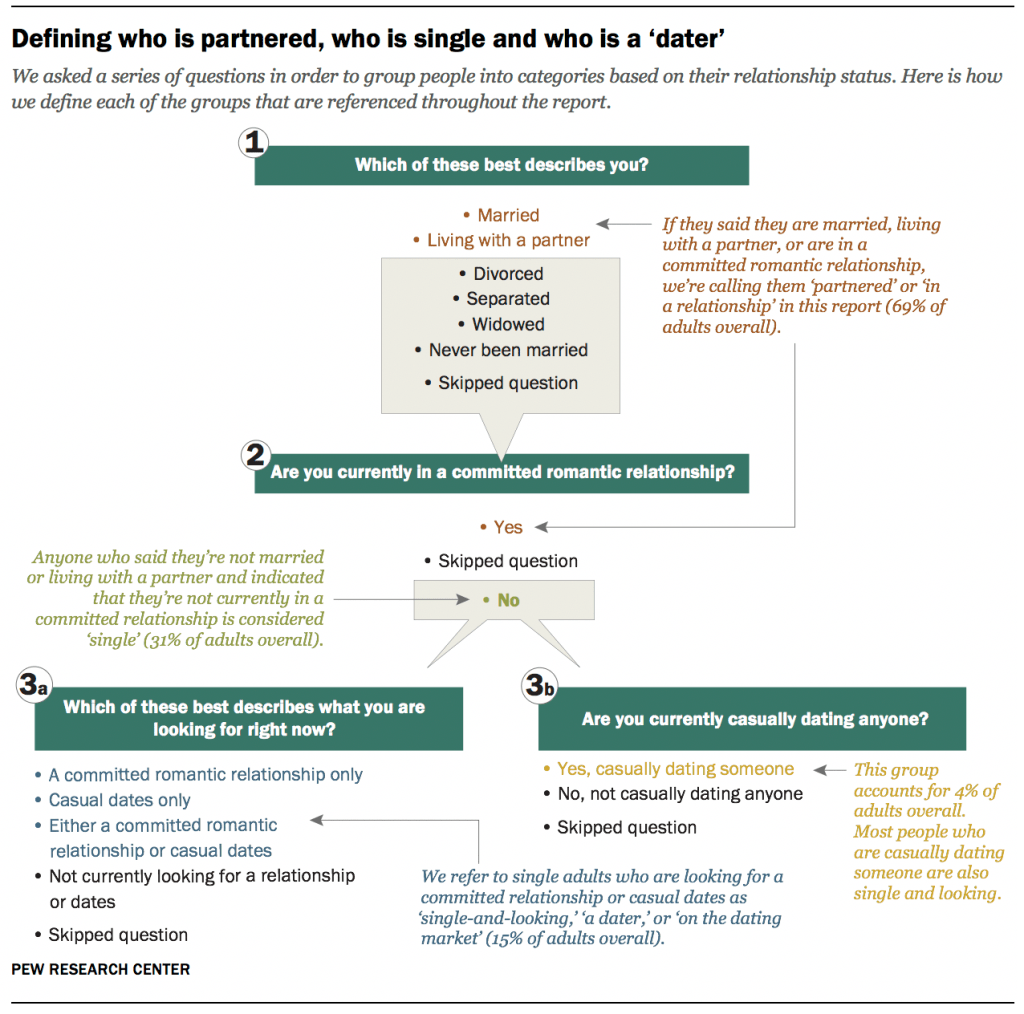
Partnered adults are those who say they are currently married, living with a partner or in a committed romantic relationship.
Single or unpartnered adults are those who say they are currently not married, living with a partner or in a committed romantic relationship. A small share of single adults report that they are casually dating someone.
Daters, single-and-looking and on the dating market all indicate that someone is currently not married, living with a partner or in a committed romantic relationship and has indicated that they are looking for a committed romantic relationship only, casual dates only or either a committed romantic relationship or casual dates.
Not dating, not looking, non-daters or not on the dating market means someone is not married, living with a partner or in a committed romantic relationship and has indicated that they are not currently looking for a relationship or dates.
Relationship, committed relationship and committed romantic relationship are used interchangeably.
Casually dating someone refers to single adults who say they are currently casually dating someone – regardless of whether they say they are looking for a committed romantic relationship, casual dates or neither.
LGB is sometimes used as a shorthand for adults who identify as lesbian, gay or bisexual, regardless of the sex of their partner, if they are partnered.
Online dating users or online daters refer to the 30% of respondents in this survey who answered yes to the following question: “Have you ever used an online dating site or dating app?”
References to White and Black adults include only those who are non-Hispanic and identify as only one race. Hispanics are of any race. The views and experiences of Asian Americans are not analyzed separately in this report due to sample limitations. Data for Asian Americans and other racial and ethnic groups are incorporated into the general population figures throughout the report.
References to college graduates or people with a college degree comprise those with a bachelor’s degree or more education. Some college includes those with an associate degree and those who attended college but did not obtain a degree. High school refers to those who have a high school diploma or its equivalent, such as a General Education Development (GED) certificate.
All references to party affiliation include those who lean toward that party. Republicans include those who identify as Republicans and independents who say they lean toward the Republican Party, and Democrats include those who identify as Democrats and independents who say they lean toward the Democratic Party.
References to those living in urban, suburban and rural areas are based on respondents’ answer to the following question: “How would you describe the community where you currently live? (1) urban, (2) suburban, (3) rural.”
As more Americans turn to online dating and the #MeToo movement leaves its imprint on the dating scene, nearly half of U.S. adults – and a majority of women – say that dating has become harder in the last 10 years.
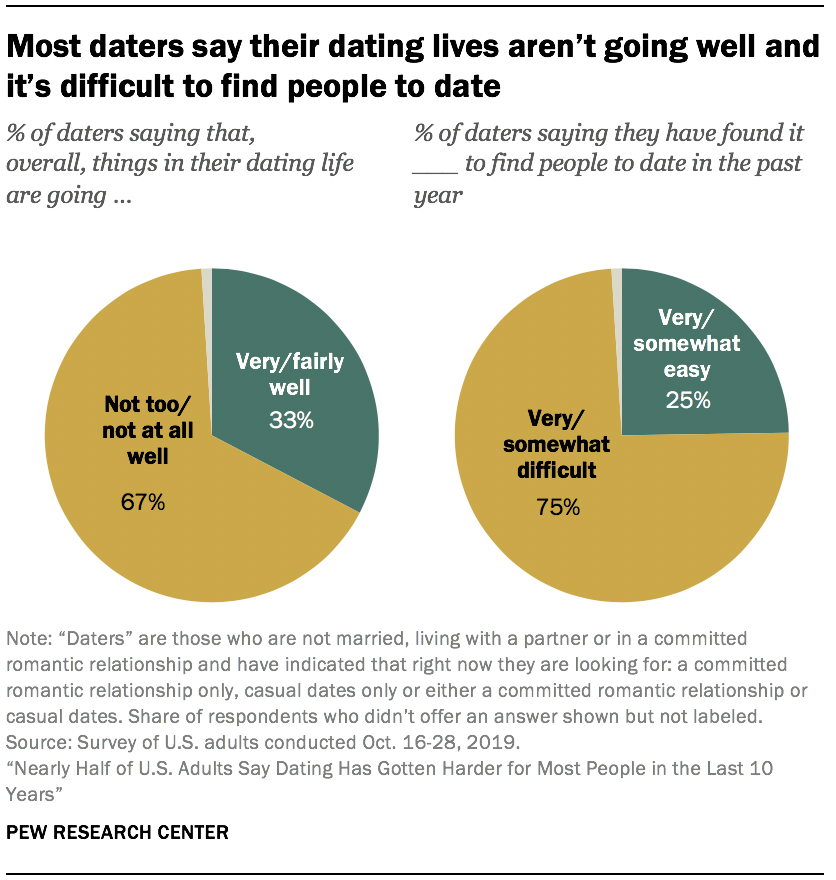
Among those who are on the dating market – the 15% of American adults who are single and looking for a committed relationship or casual dates – most say they are dissatisfied with their dating lives and that it has been difficult to find people to date, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in October 2019.1
Other publications from this survey
- The Virtues and Downsides of Online Dating
- Dating and Relationships in the Digital Age
- Lesbian, gay and bisexual online daters report positive experiences – but also harassment
- Most Democrats who are looking for a relationship would not consider dating a Trump voter
- Roughly six-in-ten online daters in the U.S. are concerned about data collection
- 10 facts about Americans and online dating
- Young women often face sexual harassment online – including on dating sites and apps
- About half of never-married Americans have used an online dating site or app
- Q&A: How and why we studied online dating in the U.S.
While single-and-looking men and women report equal levels of dissatisfaction with their dating lives and the ease of finding people to date, women are more likely to say they have had some particularly negative experiences. Most women who are currently single and looking to date (65%) say they have experienced at least one of six harassing behaviors asked about in the survey from someone they were dating or had been on a date with, such as being touched in a way that made them uncomfortable or rumors being spread about their sexual history. This compares with 50% of men who are single and looking. The pattern holds when looking at all women and men, whether they are currently on the dating market or not.
Women are also more likely to see risk – both physical and emotional – when it comes to dating. When those who say dating has become harder for most people in the last 10 years are asked to describe in their own words why they think this is the case, women are twice as likely as men to cite increased risk. For their part, men are more likely than women to say technology is a reason dating has gotten harder. Overall, 47% of Americans say dating is now harder than it was 10 years ago, while 19% say it’s easier and 33% say it’s about the same.
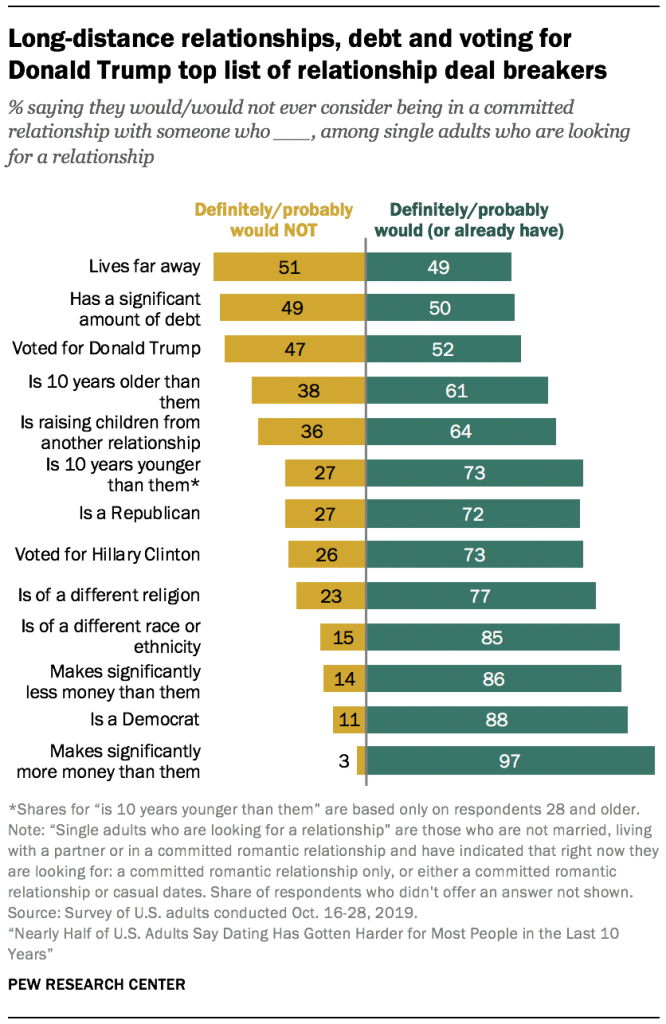
Singles who are looking for a relationship are generally open to dating people with many different traits and from a variety of backgrounds. For example, large majorities say they would consider a relationship with someone of a different religion or different race or ethnicity than them. Most also say they would seriously date someone who makes significantly more or significantly less money than them. When it comes to being in a relationship with someone who lives far away, has a significant amount of debt, or who voted for Donald Trump, however, many of those who are looking for a relationship would hesitate.
The nationally representative survey of 4,860 U.S. adults was conducted online Oct. 16-28, 2019 – before the coronavirus pandemic shook the dating landscape – using Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel.2
Among the other key findings:
Most Americans say it’s harder for men to know how to behave on dates in the era of the #MeToo movement
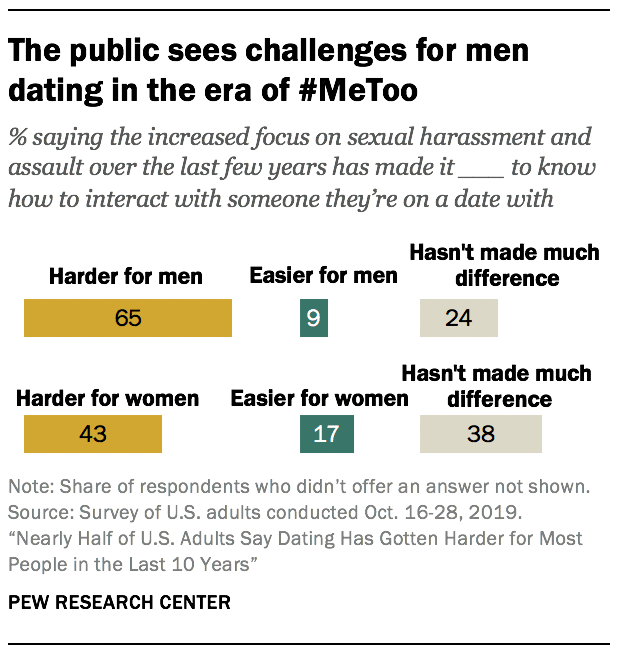
A majority of the overall public (65%) says the increased focus on sexual harassment and assault in the last few years has made it harder for men to know how to interact with someone they’re on a date with. About a quarter (24%) say it hasn’t made much difference, and 9% say it has become easier for men to know how to behave. Fewer people think this focus on harassment and assault has made it harder for women to know how to interact with someone they’re on a date with (43%), while 38% say it hasn’t made much difference for women.
Men – especially older men – and Republicans are more likely than women and Democrats to say it’s harder for men to know how to act when dating in the era of the #MeToo movement, though majorities across the board express this view. For example, 75% of men ages 50 and older say it is now harder for men to know how to behave on dates, compared with 63% of men younger than 50, 58% of women younger than 50 and 63% of women 50 and older.
Premarital sex is largely seen as acceptable, but most view sex on a first date and open relationships as taboo
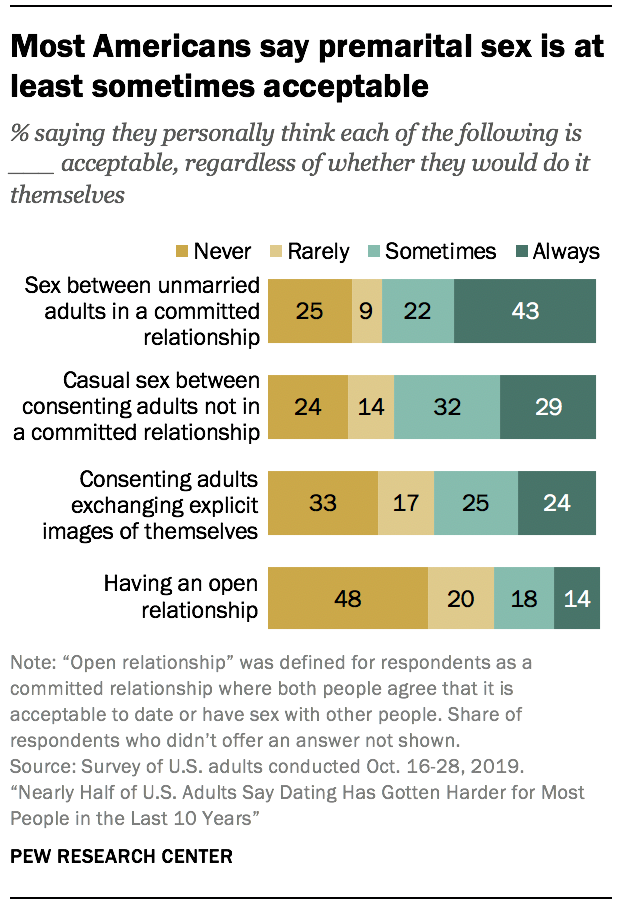
Most adults (65%) say sex between unmarried adults in a committed relationship is acceptable at least sometimes, including 43% who say this is always acceptable. Casual sex between consenting adults who are not in a committed relationship is also seen as generally acceptable (62%). About half (49%) say it is acceptable for consenting adults to exchange explicit images of themselves.
When it comes to open relationships – that is, a committed relationship where both people agree that it is acceptable to date or have sex with other people – the public is less accepting. Some 32% think this can be acceptable at least sometimes (regardless of whether they would do it themselves), while 48% say open relationships are never acceptable. Having sex on a first date is also still seen as taboo by some. While 30% say it can be acceptable under some or all circumstances, 42% say it is never acceptable.
Younger adults are more likely to see these dating norms as acceptable – sometimes dramatically so. For example, 70% of 18- to 29-year-olds say consenting adults exchanging explicit images of themselves can be acceptable at least sometimes, compared with just 21% of those ages 65 and older. Lesbian, gay and bisexual (LGB) adults also tend to be more accepting of these norms than their straight counterparts. In fact, LGB adults are the only demographic group studied in which a majority said that open relationships are always or sometimes acceptable (61% vs. 29% of straight adults).
Vast majorities say that breaking up through technology is mostly unacceptable, and few say they would ‘ghost’ someone
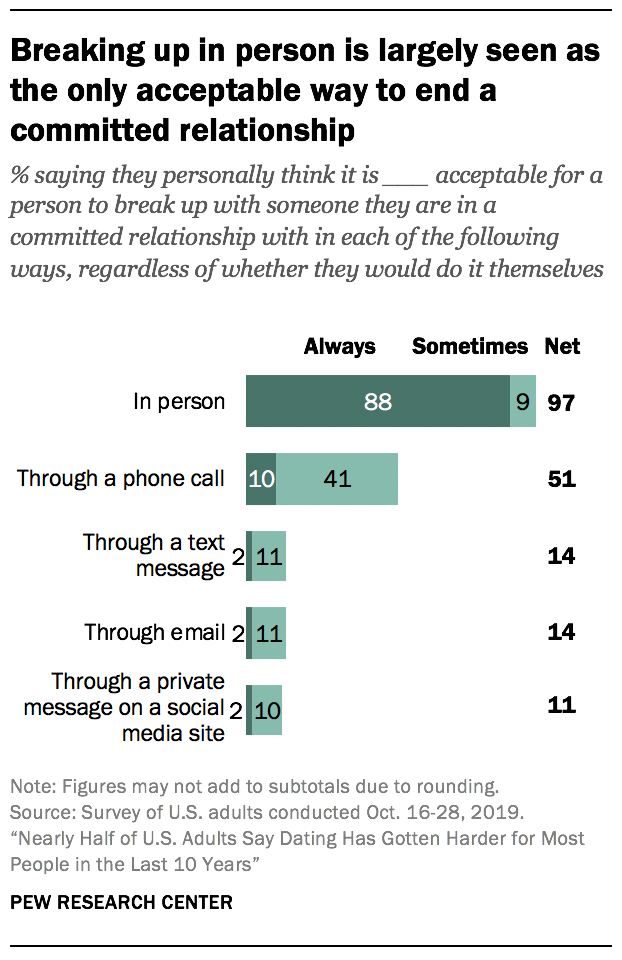
Despite concerns that Americans’ rising dependence on communicating through technology would lead to more impersonal breakups through devices, most agree that breaking up in person is the way to go. The vast majority of adults say that it is always or sometimes acceptable for a person to break up with a committed romantic partner in person (97%). About half (51%) say it is at least sometimes acceptable to break up over the phone – though only 10% say this is always acceptable. Far fewer say it can be acceptable to break up through a text message (14%), email (14%) or private message on a social media site (11%). In fact, most say it is never acceptable to end committed relationships through those forms of technology. The shares are strikingly similar when it comes to breaking up with someone a person is casually dating rather than in a committed relationship with.
The survey also asked those who are single and looking for a relationship or dates how they would let someone know they didn’t want to go out with them again after a first date. Only 8% say they would ghost someone (cut off communication). About half (52%) say they wouldn’t take the initiative to reach out but would let the other person know if they got in touch. The remaining share (40%) say they would contact the other person to let them know. Single-and-looking men are evenly split on whether they would proactively let the other person know if they didn’t want to go out again after the first date (47%) or wait for the other person to contact them before letting them know (47%). A majority of single-and-looking women (59%), on the other hand, would respond if the other person got in touch first, while 30% say they would proactively reach out and let the other person know.
Single people overall report that they don’t feel much pressure from society and the people they know to find a partner
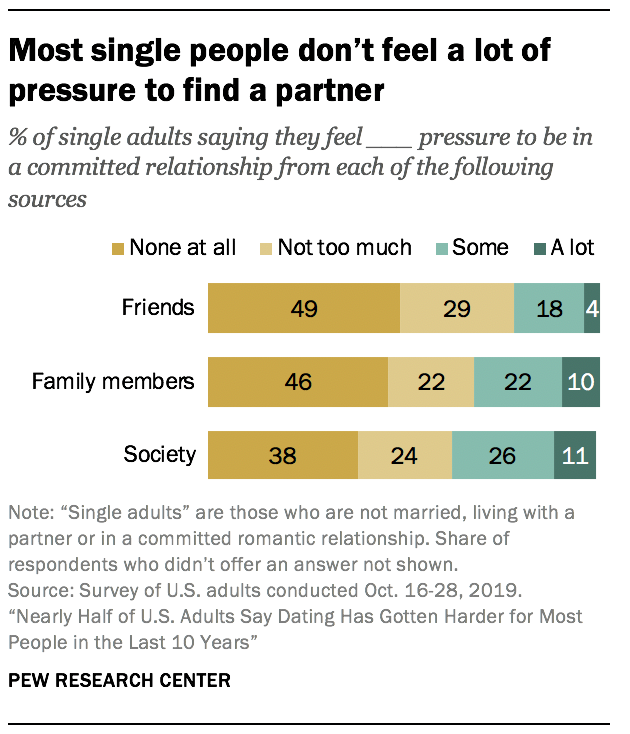
Most single people (including both those on and off the dating market) say they don’t feel a lot of pressure to find a partner from their friends, family or society in general. About two-in-ten (22%) say they feel at least some pressure from friends, while 31% say the same about family members and 37% say they feel society is pressuring them.
Feeling pressure to be in a committed relationship is highly dependent on age. Younger singles feel much more pressure from each source. For example, 53% of single 18- to 29-year-olds say there is at least some pressure from society to find a partner, compared with 42% of 30- to 49-year-olds, 32% of 50- to 64-year-olds and 21% of those ages 65 and older. In fact, a majority of singles 65 and older – the vast majority of whom are widowed or divorced, in contrast to young singles who are mostly never married – say they feel no pressure at all from each of these sources.
Single women and men give different reasons for difficulty finding people to date
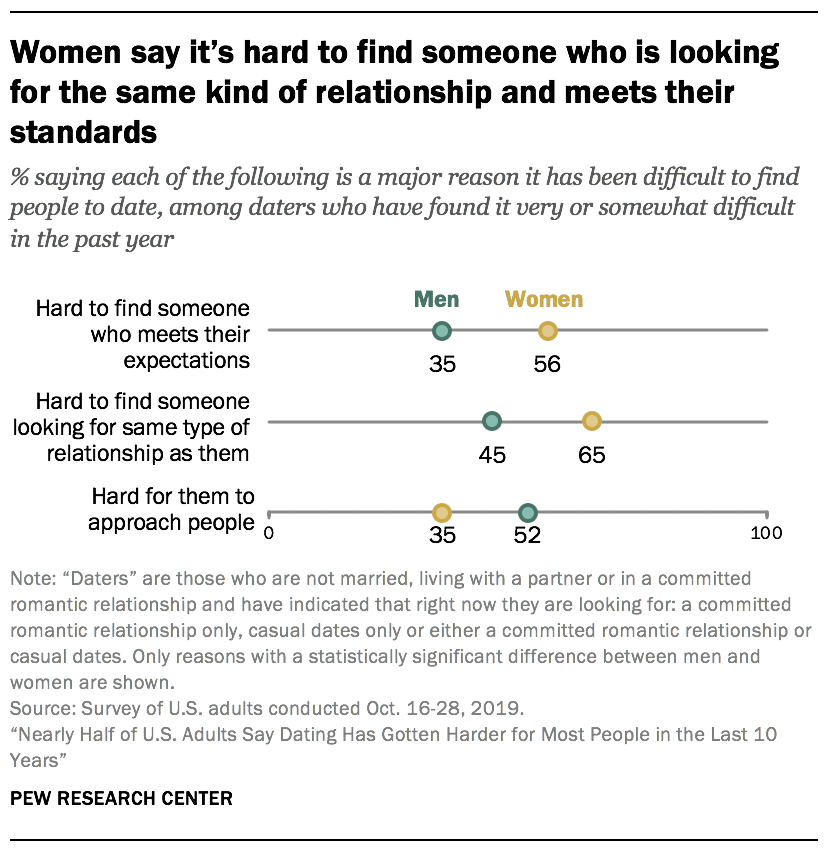
Daters who had difficulty finding people to date in the past year were asked about some of the possible reasons that might be the case. Among these daters, the most common explanations include the challenge of finding someone who is looking for the same type of relationship (53% say this is a major reason), difficulty in approaching people (46%) and trouble finding someone who meets their expectations (43%).
There are large differences by gender on this topic. Single-and-looking women are far more likely than single-and-looking men to say that trouble finding someone who was looking for the same kind of relationship or who meets their expectations are major reasons they’ve had difficulty. In turn, men are much more likely than women to say difficulty approaching people is a major reason.
Roughly one-in-ten partnered adults met their partners online, but this is far more common among some groups
A plurality of those who are married, living with a partner or in a committed romantic relationship say they first met their spouse or partner through friends or family (32%). Smaller shares say they met through work (18%) or school (17%), and still fewer met their partner online (12%).
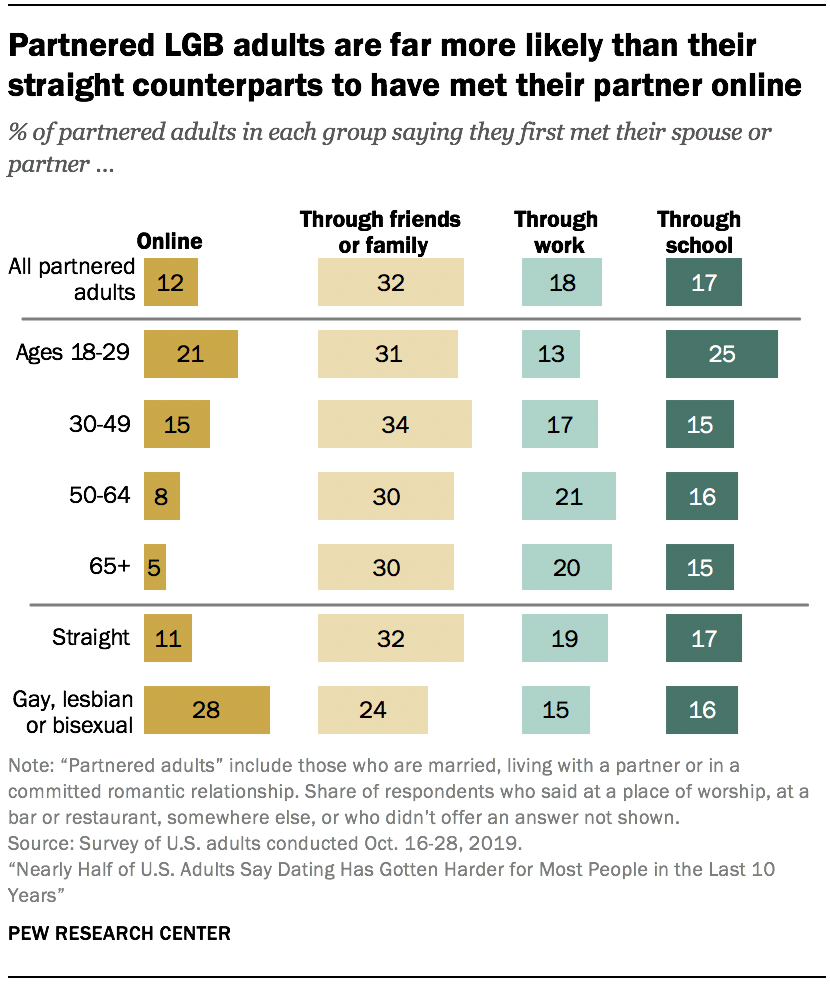
While relatively small shares of partnered adults first met their partner online, some groups are more likely to have done so. About one-in-five partnered adults ages 18 to 29 (21%) say they met their partner online, compared with 15% or fewer among their older counterparts. And LGB adults are far more likely to have first met their partner online than straight adults (28% vs. 11%).
Overall, three-in-ten adults say they have used an online dating site or app, and a majority (57%) of those users say their experiences with online dating were positive. Most also say it was easy to find people they were physically attracted to and who shared their hobbies and interests.
Online dating isn’t the only way Americans are using the internet to help them navigate the dating scene. About four-in-ten adults (38%) say they have searched for information online about someone they were romantically interested in. This is especially common among young adults: 64% of those younger than age 30 say they have done this.
Half of single adults – and a majority of single women – are not on the dating market
Fully half of single adults say they are not currently looking for a relationship or dates. Among those who are on the dating market, about half are open to either a committed relationship or casual dates.
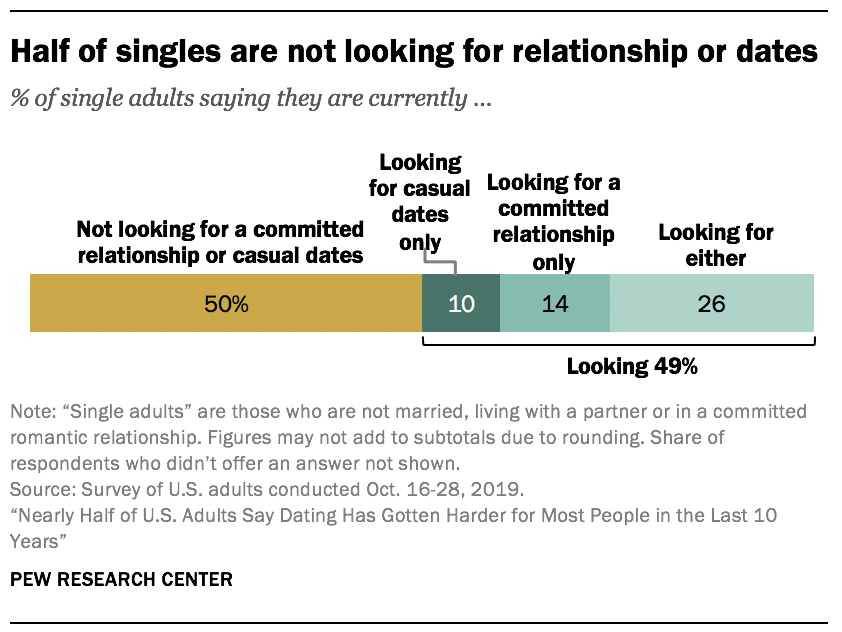
Single men are far more likely than single women to be looking for a relationship or dates – 61% vs. 38%. This gender gap is especially apparent among older singles.
Among singles who are not looking to date, having more important priorities right now and just enjoying the single life are among the most common reasons cited. Non-daters younger than age 50 are particularly likely to say they have more important priorities at the moment.